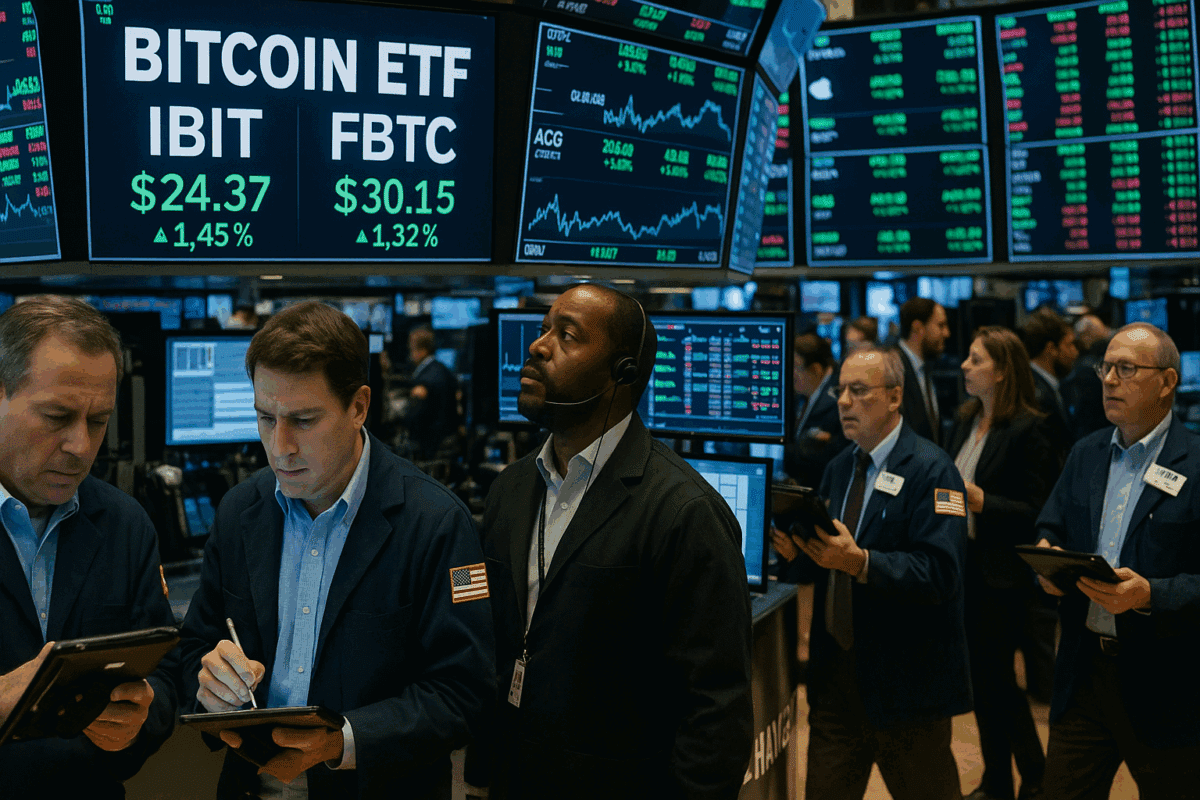
Bitcoin ETFs shot into the financial limelight, connecting the traditional money world with the often unpredictable cryptocurrency scene. People can trade these on regular stock markets, much like shares in well-known companies, and they aim to follow Bitcoin’s price changes. This allows ordinary investors to tap into Bitcoin without the usual troubles of buying it themselves, worrying about safe storage, or navigating the sometimes confusing world of crypto exchanges and digital wallets.
When the U.S. approved spot Bitcoin ETFs on January 10, 2024, it was more than a minor regulatory change; it was a landmark event, showing everyone crypto was becoming mainstream. These financial products opened doors for both individual investors and large financial institutions, making Bitcoin easier to access through a system they already knew and trusted.
Spot vs. Futures: Decoding Bitcoin ETFs
To get a handle on Bitcoin ETFs, you must first recognize two main types: spot Bitcoin ETFs and those based on futures. Understanding this difference is vital for anyone looking to invest in a Bitcoin ETF.
Spot Bitcoin ETFs: The Real Deal
- Direct Bitcoin Holdings: Spot Bitcoin ETFs are straightforward: they own actual Bitcoin. That’s what backs their value. When you purchase a share, you’re effectively buying a small fraction of the Bitcoin held by that fund. The ETF’s value, therefore, aims to closely track Bitcoin’s current market price.
- The Mechanics: The companies that offer these ETFs buy Bitcoin and keep it in highly secure storage. Think of them as digital vaults, often using methods like keeping assets offline (cold storage) and requiring multiple authorizations for any transaction (multi-signature protocols) to ensure safety. Individuals then purchase shares in these ETFs using their standard investment accounts.
- Price Reflection: The main purpose of a spot ETF is to move in tandem with Bitcoin’s price in real time. If Bitcoin’s value rises or falls, the ETF shares should reflect that, after accounting for any fees and operational expenses.
- Regulatory Embrace: Because they operate within the established financial markets, spot Bitcoin ETFs offer investors a level of protection not always found when buying crypto directly. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) monitors these products.
Futures-Based Bitcoin ETFs: The Derivative Dance
- Indirect Exposure via Contracts: Unlike spot ETFs, Bitcoin futures ETFs don’t hold any actual Bitcoin. They invest in Bitcoin futures contracts, which are agreements to buy or sell Bitcoin at a specific price on a future date.
- The Strategy: These ETFs try to match Bitcoin’s price movements by managing a collection of Bitcoin futures contracts, usually ones traded on regulated platforms like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
- “Roll” Costs & Tracking Wobbles: A key aspect—and possible drawback—of futures ETFs is the ongoing need to “roll” contracts. As current futures contracts approach their end date, the ETF has to sell them and buy new ones with later dates to stay invested. This rollover process can add costs, especially if the new contracts are more expensive than the old ones (a situation known as “contango” or “negative roll yield”). These rolling costs, plus management fees, can lead to “tracking error,” where the ETF’s performance doesn’t quite match Bitcoin’s actual spot price.
- Added Complexity: Using futures contracts makes these ETFs more complicated and can bring extra costs not usually seen with the simpler spot ETFs.
Spot vs. Futures: Key Differences
| Aspect | Spot Bitcoin ETF | Futures-Based Bitcoin ETF |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Asset | Real Bitcoin | Contracts for Bitcoin later |
| Exposure | Straight link to Bitcoin’s price | Indirect, through financial contracts |
| Price Tracking | Tries to match live price | Follows futures prices; might not match spot price perfectly, can lag |
| Complexity | Simpler, more direct | More involved due to contract juggling, market conditions like contango/backwardation |
| “Roll” Costs | Doesn’t apply | Yes, can eat into your money |
| Direct Ownership | The fund has actual Bitcoin | The fund has futures contracts, not the Bitcoin itself |
The Push and Pull: What Drives Bitcoin ETF Flows?
Money moving into (inflows) and out of (outflows) Bitcoin ETFs is influenced by a mix of market factors:
1. Market Buzz and Bitcoin’s Price Swings:
- Bullish Vibes & Price Pumps: Generally, positive feelings about Bitcoin or a big jump in its price draw money into ETFs. As Bitcoin’s value climbs, more investors want in, and ETFs look like the simplest way.
- Bearish Clouds & Price Dumps: On the other hand, if Bitcoin’s price falls sharply or the whole crypto market takes a hit, investors might rush to sell (outflows). People might sell ETF shares to limit losses or reduce risk. A steep drop in Bitcoin’s price often makes big institutional investors hesitate, leading to ETF withdrawals.
- Profit Skimming: After a strong price run, some investors will naturally sell their ETF shares to lock in profits, causing outflows.
2. The Create/Redeem Engine (Especially for Spot ETFs):
This is the clever system that keeps an ETF’s share price close to Bitcoin’s actual price.
- Inflows (Creation): When lots of people want to buy ETF shares, sometimes pushing the ETF’s market price above the value of the Bitcoin it holds (its Net Asset Value or NAV), Authorized Participants (APs) step in. These APs, usually very large financial firms, buy Bitcoin on the open market and give it to the ETF provider. In exchange, they get brand-new ETF shares. The APs then sell these new shares on the stock market, increasing supply and helping to bring the ETF share price back in line with its NAV. This process brings more Bitcoin into the ETF’s holdings.
- Outflows (Redemption): If demand for ETF shares drops, and the market price falls below its NAV, APs might buy these cheaper ETF shares from the market. They then give these shares back to the ETF provider for an equivalent amount of Bitcoin. The APs can then sell this Bitcoin. This reduces the number of ETF shares available and helps the share price match the NAV, resulting in Bitcoin leaving the ETF’s holdings.
- Cash vs. In-Kind: Many standard ETFs use “in-kind” redemptions (where APs receive the actual assets the ETF holds). However, some Bitcoin ETFs, especially when they first launched or due to certain rules, might use “cash redemptions.” In this case, the ETF provider sells the Bitcoin to get cash for the AP. The “in-kind” method is often preferred because it can be more tax-efficient and less disruptive to the market.
3. The Arbitrage Game:
Differences in price between the ETF and Bitcoin’s spot price, or between spot ETFs and futures contracts, can open up chances for traders to profit.
- Basis Trading: Traders often do “basis trading.” This might mean buying the actual asset (maybe through an ETF) and at the same time selling futures contracts if the futures price is much higher than the spot price (a positive basis). The aim is to make money on the price difference when the contract ends. Or, they might sell the asset and buy futures if the basis is negative. The close price relationship between spot Bitcoin ETFs and CME futures contracts helps these trades happen.
- Flow Impact: Arbitrage activities can significantly affect ETF inflows and outflows. If an ETF is trading for more than its NAV, arbitrage traders might create new shares (causing inflows) to profit from that difference. If it’s trading for less, they might redeem shares (causing outflows). Some analysis indicates that a good portion of the initial money flowing into Bitcoin ETFs came from these arbitrage trades rather than from people simply betting on Bitcoin’s long-term rise.
4. The Institutional Herd:
The entry of institutional investors is a huge factor for ETF flows. Their involvement is often seen as a sign that the crypto market is maturing.
- Institutions might follow trends; they could invest heavily when prices are rising (increasing inflows) and pull out when trends change (leading to outflows).
- Data on ETF flows is now closely watched as a sign of what institutions are thinking. Large inflows from institutions can boost market confidence, while big outflows can be a warning.
5. The Regulatory Pendulum:
Official announcements and approvals from regulators greatly affect investor confidence and, as a result, ETF flows. The SEC’s approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in the U.S. was a clear example, causing a surge of inflows. On the flip side, unclear rules or crackdowns can make investors nervous and lead to outflows.
6. Macroeconomic Tremors:
The overall economic situation—things like inflation numbers, talk about Federal Reserve policies, or global trade disputes—can change how willing investors are to take risks and thus affect flows into assets like Bitcoin ETFs. A general “risk-off” feeling in traditional markets can easily spread to crypto, leading to outflows.
7. Liquidity & Trading Heat:
More liquidity in Bitcoin ETFs usually means smaller differences between buying and selling prices (tighter bid-ask spreads) and more accurate tracking of Bitcoin’s price. High trading activity and plenty of liquidity can attract more investors, which could lead to more stable prices and better price discovery for Bitcoin itself. Low liquidity, however, can widen spreads and make it more expensive for investors to trade ETF shares.
8. The Fee Skirmish & Competition:
The boom in Bitcoin ETFs has sparked intense competition among providers, often resulting in a rush to offer the lowest management fees (expense ratios). Lower fees can make certain ETFs more appealing, which can influence how inflows are distributed among different funds.
In short, Bitcoin ETFs present a new and increasingly chosen way to invest in Bitcoin. Spot ETFs give direct exposure by holding Bitcoin, while futures ETFs use derivative contracts, each with its own way of working and associated costs. The money flowing into and out of these products is always changing, pushed and pulled by a strong combination of market mood, arbitrage chances, institutional moves, the mechanics of share creation and redemption, and the wider regulatory and economic environment. Watching these flows provides valuable insights into investor thinking and potential future directions in the Bitcoin market.
The Long Road to Redemption: A Decade-Long Saga for Spot Bitcoin ETF Approval
The path to getting spot Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) approved in the United States was a long and difficult journey, a multi-year struggle filled with regulatory obstacles and disappointments. It took over ten years, showing the determination of asset managers and how understanding of this new digital asset type evolved.
Early Forays and a Wall of Rejections (2013-2022)
- The Genesis: The effort started back in 2013 when Cameron and Tyler Winklevoss, the entrepreneurs behind the Gemini crypto exchange, submitted the very first application for a spot Bitcoin ETF. Around that same time, Grayscale Investments introduced its Bitcoin Investment Trust (GBTC) in 2013, a private trust that it later hoped to turn into a proper ETF.
- The SEC’s “No” Chorus: For years, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) consistently rejected these and later proposals from many hopeful asset managers. By some counts, the SEC turned down over 16 different Bitcoin ETF applications.
- The SEC’s Core Hang-ups: The agency’s refusals stemmed from several main worries:
- Manipulation & Fraud Fears: The SEC repeatedly voiced concerns that Bitcoin markets were susceptible to manipulation and fraudulent activities. The agency wasn’t convinced that proposals could adequately protect against such practices.
- Investor Protection Imperative: Protecting investors from what it saw as the dangers of the volatile and still-young cryptocurrency market was a top priority for the SEC.
- Custody Conundrums: Securely storing the underlying Bitcoin was another major issue.
- Surveillance-Sharing Void: The SEC consistently asked for comprehensive surveillance-sharing agreements with a “regulated market of significant size” related to Bitcoin. This, the SEC claimed, was vital to detect and prevent fraud. Applicants often pointed to the Chicago Mercantile Exchange’s (CME) Bitcoin futures market, but the SEC initially felt it didn’t meet the “significant market test.”
The Tide Turns: Futures ETFs and Grayscale’s Legal Gambit
- Futures ETFs Get the Nod (2021): A notable change in the SEC’s stance came in October 2021. The agency approved the first Bitcoin futures ETFs. These products don’t hold actual Bitcoin but instead invest in Bitcoin futures contracts traded on the regulated CME. Many saw this approval as a quiet acknowledgment of Bitcoin-linked investment products.
- Grayscale’s Courtroom Victory (August 2023): Grayscale Investments didn’t accept the rejection of its GBTC-to-ETF conversion. It sued the SEC. In a key ruling in August 2023, a federal appeals court agreed with Grayscale, calling the SEC’s rejection “arbitrary and capricious.” The court stated the SEC hadn’t properly explained why it approved Bitcoin futures ETFs while denying Grayscale’s spot Bitcoin ETF, especially given the close price relationship between spot Bitcoin and CME Bitcoin futures. This ruling greatly increased pressure on the SEC. The agency chose not to appeal this decision in October 2023.
The Final Stretch to Approval (Late 2023 – Early 2024)
- Momentum Builds: After Grayscale’s win, the push for spot Bitcoin ETF approval became unstoppable. Financial giants like BlackRock, Fidelity, and Invesco had applications pending. BlackRock’s filing in June 2023 was especially important, given its status as the world’s largest asset manager and its strong track record with ETF approvals.
- Addressing SEC’s Lingering Doubts: Applicants worked quickly to address the SEC’s remaining concerns, finalizing important paperwork. The main focus was on showing a strong enough connection between spot Bitcoin prices and CME Bitcoin futures prices, suggesting that CME futures market surveillance could indeed help detect manipulation in the spot market.
- Cash-Only Creates/Redeems: The SEC ultimately required a cash-only creation and redemption process for the approved spot Bitcoin ETFs. This means Authorized Participants (APs) exchange cash for ETF shares, and vice versa, instead of directly dealing with Bitcoin. This was likely a measure to reduce risks related to money laundering or self-dealing.
The Historic Green Light (January 2024)
- Approval Day: On January 10, 2024, the SEC approved 11 spot Bitcoin ETFs for listing and trading on major U.S. exchanges. Trading for the first ten began the very next day.
- SEC’s Rationale Shift: In its approval order, the SEC focused on the high correlation between spot Bitcoin prices and CME Bitcoin futures prices. It concluded that CME surveillance could effectively help detect manipulation in spot Bitcoin markets.
- Gensler’s Cautious Stance: Despite the approvals, then-SEC Chair Gary Gensler was quick to state that the agency “did not approve or endorse Bitcoin.” He repeated warnings about the “myriad risks associated with Bitcoin and products whose value is tied to crypto,” calling Bitcoin a “speculative, volatile asset” also used for illegal purposes.
Global Precedents
It’s important to remember that the U.S. wasn’t the first country to approve these. Canada launched the world’s first spot Bitcoin ETF way back in February 2021. Europe saw its first spot Bitcoin ETF go live in 2023, and Australia listed its first Bitcoin ETF in 2022.
The Story Continues
- Market Reaction: The U.S. spot Bitcoin ETF approval was seen as a major turning point, opening the way for a wider range of investors, including large institutions, to access Bitcoin through traditional brokerage accounts. Billions of dollars flowed in within the first few months.
- Ethereum ETFs Follow: Building on this, the SEC also approved Ethereum (ETH) spot ETFs in May 2024.
- Ongoing Regulatory Gaze: Despite these approvals, the regulatory story for crypto assets is far from finished. Discussions about issues like in-kind redemptions for Bitcoin ETFs continue. SEC Commissioner Hester Peirce, known for her crypto-friendly stance, publicly criticized the agency’s handling of the Bitcoin ETF approval process, calling it “terribly mismanaged” and arguing it had hindered innovation.
In summary, the U.S. approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs was a landmark event, the result of a decade of persistent effort by asset managers and a crucial legal fight that forced the SEC to reconsider its long-standing objections. While worries about market manipulation and investor protection remain, these approvals clearly signal a growing mainstream acceptance and integration of cryptocurrencies into the traditional financial system.
The Bitcoin ETF Arena: Players, Fees, and Fund Flow Battles
The world of Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) has grown explosively, especially after the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved a group of spot Bitcoin ETFs in January 2024. This key decision opened a regulated way for mainstream investors to get into Bitcoin through their regular brokerage accounts, avoiding the often difficult process of direct crypto ownership and storage. Here’s an update on the major Bitcoin ETFs, their creators, fee competitions, and a comparison of their Assets Under Management (AUM) and how funds are flowing.
Major Bitcoin ETFs, Their Architects, and the Price of Admission (Fees)
The competition among Bitcoin ETF providers quickly turned into a “fee war,” with many companies launching with extremely low or even zero fees for an initial period to attract early investors. Many of these introductory offers have since ended. Fees are a major point of competition, as they can significantly reduce long-term returns.
Here’s a look at some well-known U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs and their fee structures (as of early 2025; fees can change):
- Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC): A long-time player, GBTC changed from a trust to an ETF. It started with the highest fee at 1.50%. Grayscale has since indicated a change in strategy, announcing plans for a Bitcoin Mini Trust (BTC) with a much lower proposed fee of 0.15%.
- iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) by BlackRock: This giant quickly became a leader, surpassing GBTC in AUM. IBIT began with an introductory fee of 0.12% for the first 12 months or $5 billion in assets, which was set to change to 0.25%. Its current actual fee is around 0.21% due to its large AUM.
- Fidelity Wise Origin Bitcoin Fund (FBTC): Another major competitor with substantial AUM. Its fee is a clear 0.25%.
- ARK 21Shares Bitcoin ETF (ARKB): A collaboration between ARK Invest and 21Shares. The fee is 0.21%.
- Bitwise Bitcoin ETF (BITB): Initially had a zero-fee period for the first $1 billion in AUM, then 0.20%. The standard fee is now 0.20%.
- VanEck Bitcoin Trust (HODL): VanEck notably extended its zero-fee offer until January 2026 (or until $2.5 billion AUM), after which the fee will be 0.20%.
- Franklin Templeton Digital Holdings Trust (EZBC): Offers one of the lowest ongoing fees at 0.19%.
- Invesco Galaxy Bitcoin ETF (BTCO): Has a fee of 0.25%, though some sources list it closer to 0.21%.
- WisdomTree Bitcoin Fund (BTCW): Carries a fee of 0.30%, though some data suggests 0.25%.
- Valkyrie Bitcoin Fund (BRRR): Priced at 0.25%.
- Hashdex Bitcoin ETF (DEFI): This fund switched from a futures-based approach. Its fee is higher at 0.90%.
Beyond the Sticker Price: Investors should also consider potential trading commissions (though many brokerages now offer commission-free ETF trading), bid-ask spreads (the difference between buying and selling prices), and custody fees (often included in the expense ratio).
The Global Picture: While the U.S. market has made headlines, Bitcoin ETPs (Exchange Traded Products, a wider category including ETFs and ETNs – Exchange Traded Notes) have been available in other areas for longer. Canada, for example, approved its first spot Bitcoin ETF back in 2021. Europe also has Bitcoin ETPs, although EU rules currently create challenges for Bitcoin ETFs that directly hold the crypto. Chile also has a Bitcoin ETF trading on the Santiago Stock Exchange.
AUM & Fund Flow Showdown
The launch of U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs brought a huge wave of money.
- New Titans Emerge: BlackRock’s IBIT and Fidelity’s FBTC quickly became leaders in attracting new assets. IBIT impressively reached $10 billion in AUM in a record seven weeks and later overtook GBTC to become the largest spot Bitcoin ETF by AUM.
- GBTC’s Bleed: Grayscale’s GBTC, despite its large initial AUM (from its time as a trust), saw a significant amount of money leave. This outflow is mostly due to its higher fees compared to the new, more competitively priced options.
- Market-Wide Impact: Together, U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs saw tens of billions of dollars in net inflows within their first year. The trading volume on their first day alone was enormous, showing strong investor interest.
- Flow Trackers: Many platforms and financial news outlets now offer trackers for Bitcoin ETF AUM and daily/weekly inflow and outflow data. These trackers provide a clear picture of changing investor sentiment and how assets are being moved within this new ETF category.
Key Pointers for Investors
- Spot vs. Futures – Know the Difference: Spot Bitcoin ETFs involve direct Bitcoin ownership and aim to closely follow its price. Bitcoin futures ETFs, available in the U.S. before spot versions, invest in Bitcoin futures contracts. These futures-based products can have higher operating costs and might not track Bitcoin’s price as accurately due to issues like contract rollover.
- Who’s Minding the Coins? (Custodianship): Most spot Bitcoin ETFs use third-party custodians to keep the underlying Bitcoin safe. Coinbase is a major custodian for many of these ETFs. Some issuers, like Fidelity, use their own custody solutions.
- The Tracking Gap (Tracking Error): While low fees are attractive, investors must also check how well an ETF follows Bitcoin’s actual price changes. Significant tracking errors can reduce returns, even with low fees.
- Liquidity & Trading Volume – The Smoother Ride: ETFs with higher AUM and strong trading volumes usually offer better liquidity. This means it’s easier to buy and sell shares at the prices you want.
The arrival of spot Bitcoin ETFs, especially in the U.S., is a major step in the crypto market’s growth. It offers a more accessible and regulated way for a wider range of investors to get Bitcoin exposure. However, like any investment, careful research and a clear understanding of individual risk tolerance and investment goals are essential.
Bitcoin ETFs Ignite the Market: Price, Volume, and Liquidity Shifts
The U.S. launch of spot Bitcoin Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) on January 11, 2024, was more than a new product; it was a major event for the cryptocurrency market. These tools give investors a way to access Bitcoin’s price changes through traditional brokerage accounts, removing the need to directly own and manage the digital currency. The immediate and short-term effects on Bitcoin’s price, trading volume, and market liquidity have been significant.
Impact on Bitcoin’s Price: A Rollercoaster Ride with an Upward Tilt
- Pre-Approval Rally & “Sell the News” Dip: Bitcoin’s price rose considerably leading up to the ETF approvals, reaching over $49,000 on January 11th, its highest point since December 2021. However, once the ETFs started trading, the price experienced a typical “sell the news” drop. Despite this initial setback, Bitcoin quickly recovered and began a new upward trend, breaking previous all-time highs later in the year, climbing past $73,000 in March 2024. Some unconfirmed reports even suggested prices briefly hit as high as $108,000 in mid-December 2024.
- Fresh Demand & The “Supply Squeeze” Narrative: The ETFs created a new source of demand, especially from mainstream and institutional investors who preferred a regulated investment product. This increase in demand, combined with Bitcoin’s limited supply, has been identified as a key reason for price increases. Even before the launch, analysts were discussing price impact, with some predicting targets from $42,000 to $100,000 or even higher in the long run. Galaxy Digital, for instance, calculated a potential +6.2% price increase in the first month and a possible +74% rise in the first year.
- Market Validation & Confidence Boost: The SEC’s approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs was widely seen as a validation of Bitcoin’s legitimacy within the established financial system. This perceived endorsement seems to have significantly boosted investor confidence.
Impact on Trading Volume: A Gusher of Activity
- Trading Frenzy Unleashed: The launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs caused a dramatic increase in Bitcoin transfer volumes and overall trading activity. Daily ETF volumes soared, approaching an incredible $10 billion in March 2024 and consistently trading in the billions.
- Focus on U.S. Market Hours: Trading volumes on crypto exchanges, especially those that feed into Bitcoin benchmark rates, increased, particularly during U.S. market hours. A notable rise in volume occurred during the important “fixing window” between 3 p.m. and 4 p.m. New York time, directly related to the ETFs’ net asset value (NAV) calculation.
- Weekend Trading Wanes: The introduction of spot ETFs appears to have sped up a decline in Bitcoin’s weekend trading, with the share of weekend volume reaching an all-time low in 2024.
- Outshining Other ETFs: In their initial trading period, the combined trading volumes for the new spot Bitcoin ETFs ranked impressively high compared to all U.S.-listed ETFs. They even surpassed the largest non-crypto commodity-based ETF (GLD) and the largest Bitcoin futures-based ETF ($BITO) during the same period.
Impact on Market Liquidity: Deepening the Pool
- Liquidity Enhancement: Spot Bitcoin ETFs have generally been seen as a positive for market liquidity. By making Bitcoin easier to buy and sell through familiar brokerage channels, ETFs have expanded the investor base and made trading smoother.
- Steadier Prices & Price Discovery: The improved liquidity from these ETFs is expected to lead to more stable prices and better price discovery in the broader Bitcoin market.
- U.S. Market Concentration: The positive effect on liquidity has been most noticeable in U.S. markets, especially on weekdays and around the U.S. market close. However, this concentration could mean increased volatility outside of U.S. trading hours.
- Market Makers’ Role: ETF trading can boost spot Bitcoin liquidity as ETF liquidity providers and market makers actively trade and hedge their positions in the spot market.
Short-Term Hurdles and Hazards
- Volatility Still a Beast: While ETFs might contribute to long-term stability, Bitcoin’s well-known price swings remain a big risk for ETF investors. Ironically, the inflow of large amounts of money could also increase short-term volatility.
- “Sell the News” Hangovers: As seen, markets can experience short-term price drops immediately after major positive news like ETF approvals.
- Regulatory Fog: Despite the approvals, the changing regulatory situation for cryptocurrencies continues to pose a risk. SEC Chairman Gary Gensler, even while approving the ETFs, specifically did not endorse Bitcoin and issued warnings to investors.
In conclusion, the arrival of spot Bitcoin ETFs has had a dynamic and varied impact on the Bitcoin market in the immediate and short term. It has generally pushed prices up (despite initial dips), greatly increased trading volumes (especially during U.S. market hours), and improved market liquidity. The move is widely praised as a significant step towards mainstream adoption and market maturity for Bitcoin. However, smart investors will stay aware of the inherent volatility and changing regulatory landscape associated with this new asset class.
Institutional Stampede: The Driving Force Behind Bitcoin ETF Inflows
The flood of money into Bitcoin ETFs since their prominent launch, particularly in early 2024, marks a major change in cryptocurrency investment. A close examination of data and market commentary shows that institutional investors are increasingly leading these inflows, though interest from individual investors remains a strong underlying factor.
Who’s Fueling the Bitcoin ETF Rocket?
- The Rise of Institutional Titans: The main force behind the explosive ETF inflows is the growing acceptance and strategic use of Bitcoin by large institutions. This includes asset managers, hedge funds, and even some pioneering pension funds venturing into crypto.
- The introduction of spot Bitcoin ETFs offered a regulated, easy-to-use, and familiar investment method for these institutions. It allowed them to get Bitcoin exposure without dealing with the complexities of direct ownership, secure storage, or crypto exchanges.
- Financial giants like BlackRock have entered the field with products like the iShares Bitcoin ETF (IBIT). IBIT’s rapid growth, quickly accumulating billions in assets, highlights the strong institutional demand. In an impressive achievement, BlackRock’s IBIT became the fastest ETF ever to reach $10 billion in Assets Under Management (AUM).
- There are rumors that the “Big Four” wirehouses—Merrill Lynch, Morgan Stanley, Wells Fargo, and UBS—might start trading Bitcoin ETFs by the end of 2025. Such a development would bring in another massive wave of institutional money.
- Data indicates a clear shift in ETF ownership, with institutional and wealth advisory clients now holding a larger share compared to the initial retail-driven boom.
- Publicly traded companies have also been observed steadily increasing their Bitcoin holdings.
- Retail Still in the Game: While institutional investors are making big moves, individual investors continue to contribute significantly to ETF inflows.
- ETFs offer a much simpler way for traditional investors, who might be put off by the perceived complexities of direct cryptocurrency trading, to get involved.
- The constant media attention on Bitcoin’s price movements and the ETF launches themselves undoubtedly sparks retail interest.
- However, some analysis suggests that a large part of this retail interest comes from individuals already familiar with crypto. The percentage of completely new retail investors entering the market only through ETFs seems to be smaller, though recent data from May 2025 points to strong inflows from “first-time buyer” retail wallets.
- Credibility Surge & Mainstream Embrace: The regulatory approval for Bitcoin ETFs from bodies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has given Bitcoin a significant degree of legitimacy as a real asset class. This, in turn, has reassured investors about its long-term prospects.
- Market Momentum & Performance Allure: Bitcoin’s history of dramatic price growth has created a powerful wave of optimism, attracting investors eager to benefit from its upward trend. The expectation of continued, strong ETF inflows has become a common theme in market discussions.
- The Supply Squeeze Effect: Increased institutional investment through ETFs, where providers typically store large amounts of Bitcoin in cold storage, is reducing the available supply of Bitcoin. This shrinking circulating supply, met with rising demand, can act as a strong price driver.
Macroeconomic Winds Influencing the Flow
- Inflation’s Shadow: Bitcoin is often described as a hedge against inflation, frequently compared to “digital gold.”
- Times of rising inflation or the expectation of future inflation can increase demand for Bitcoin as a store of value, potentially directing more funds into ETFs.
- Conversely, a low-inflation environment might see investors preferring more traditional assets.
- The Interest Rate Compass: Central bank interest rate policies heavily influence investment decisions.
- Lower interest rates, or the expectation of rate cuts, can make riskier assets like Bitcoin seem more attractive as investors search for higher returns. This can lead to a surge in ETF inflows.
- Conversely, rising interest rates can make lower-risk assets more appealing, potentially diverting money away from Bitcoin and its ETFs.
- The Sentiment Thermometer: General market sentiment towards cryptocurrencies and risk assets overall greatly affects capital flows.
- Positive news, regulatory advances, and bullish price movements can create a positive feedback loop, attracting more investment.
- Conversely, negative headlines, regulatory crackdowns, or sharp price drops can trigger outflows or reduce inflows. ETF flow data itself is increasingly watched as a key indicator of prevailing market sentiment.
- Global Jitters & Geopolitical Chess: During times of economic instability or increased geopolitical tensions, some investors may turn to alternative assets like Bitcoin as a potential safe haven or a way to diversify their portfolios. This can contribute to ETF inflows.
- The Regulatory Weather Vane: Regulatory clarity, or even the expectation of it, significantly impacts investor confidence and institutional involvement.
- Positive regulatory developments, such as the ETF approvals, can unleash a wave of inflows.
- Conversely, ongoing uncertainty or clearly negative regulatory actions can reduce enthusiasm. The perceived pro-crypto stance of certain political administrations is also seen by some investors as a bullish sign.
- The Dollar’s Dance: A weakening U.S. dollar can sometimes correlate with increased interest in assets like Bitcoin as an alternative store of value.
Current Pulse & Future Gazing
As of early to mid-2025, market reports suggest continued strong institutional interest and widespread expectations of significant net inflows into Bitcoin ETFs throughout the year, possibly even surpassing the records set in 2024. Some analysts predict substantial AUM growth for Bitcoin ETFs by the year’s end. BlackRock, a key player, noted that the newly launched spot Bitcoin ETPs saw unprecedented adoption in 2024, effectively connecting to traditional finance and sparking a surge of interest from end investors, wealth advisors, and institutional capital.
However, it’s important to be cautious. Some analysts point to a potential short-term slowdown in institutional momentum, despite overall long-term confidence. The market also remains highly sensitive to volatility caused by macroeconomic changes or unexpected regulatory news. Furthermore, concerns exist that continued, massive ETF inflows could weaken Bitcoin’s status as a pure macroeconomic hedge if its price becomes too closely tied to traditional stocks.
In essence, the current wave of Bitcoin ETF inflows is largely driven by a significant and growing institutional presence, made possible by the accessibility and regulated nature of these new investment products. While retail investors remain active, the sheer amount of institutional money being invested is a defining characteristic. These flows are further shaped by a complex mix of macroeconomic factors, with inflation, interest rates, and overall market sentiment playing key roles in investor decisions.
Bitcoin ETFs and Volatility: A Tangled Relationship
The introduction of Bitcoin Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) has been a major event in cryptocurrency’s story, and their effect on Bitcoin’s well-known price swings is a hot topic for ongoing analysis and debate among market watchers. Here’s a closer look at the complex connection between Bitcoin ETF inflows and price volatility.
1. Unlocking Access & Boosting Adoption:
- Bitcoin ETFs have made Bitcoin more accessible, allowing mainstream investors to get exposure through their regular brokerage accounts. This has removed technical hurdles like managing digital wallets or dealing with often-complex crypto exchanges. This wider accessibility can logically lead to broader adoption and, as a result, potentially higher demand for Bitcoin.
- The regulatory approval and subsequent launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs have also been widely seen as a validation of Bitcoin’s legitimacy within the established financial system, potentially boosting investor confidence.
2. Liquidity Injection & The Quest for Stability:
- A common belief is that Bitcoin ETFs could significantly improve market liquidity by attracting a more diverse group of investors and increasing trading volumes. Generally, higher liquidity tends to lead to more stable prices and smoother price discovery.
- Some market analysts argue that a steady flow of funds into Bitcoin ETFs, especially from institutional investors with a longer-term view, can act as a stabilizing force. This capital can absorb selling pressure and potentially reduce erratic price swings.
- The mere presence of large institutional players, often investing through these ETF structures, may help lessen extreme price volatility.
3. The Inflow-Price Connection: What the Data Suggests
- Several studies indicate a connection between Bitcoin ETF inflows and Bitcoin’s price movements. For instance, one research paper highlighted a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.82 between the two, suggesting that significant ETF inflows are often followed by a rise in Bitcoin’s price.
- Another analysis, using a Vector Autoregression (VAR) model, found that the previous day’s ETF inflows positively affect the current day’s Bitcoin price changes. This supports the idea that ETF activity does influence Bitcoin’s market behavior.
- However, it’s important to note that the strength of this connection can vary. An analysis by Kaiko found a relatively modest R-squared value of 0.32 between on-chain net flows for U.S. Bitcoin Spot ETFs and daily BTC-USD price changes. While this suggests some relationship, it’s not overwhelmingly strong. Research from FalconX also noted that while a statistically significant relationship exists, less than 10% of the change in prices could be explained by the change in net flows when looking at 7-day periods, though this correlation seemed to be strengthening over time.
4. Factors Stirring the Volatility Pot:
- Market Sentiment & Speculative Fervor: Bitcoin’s price remains very sensitive to prevailing market sentiment and speculative trends. Positive news, like ETF approvals, can ignite bullish momentum, while negative developments can trigger sharp declines.
- Institutional Appetite: Strong institutional interest, shown by large inflows into ETFs managed by financial giants like BlackRock, can signal bullish sentiment and contribute to price stability or upward trends.
- The Broader Market Climate: Wider economic conditions, including worries about stagflation or fluctuations in traditional stock markets, can influence investor caution towards riskier assets like Bitcoin. This, in turn, affects ETF flows and price volatility.
- Regulatory Winds: Regulatory actions and the level of clarity (or lack thereof) significantly impact Bitcoin’s price and the viability of ETFs.
- “Weak Hands” vs. Long-Term Conviction: Some argue that ETF demand is gradually replacing shorter-term, more speculative holders with investors who have a longer-term perspective. This shift could potentially lead to less panic selling and increased stability.
5. The Other Side of the Coin: Potential for Amplified Swings
- While many observers highlight the potential stabilizing effect of ETFs, Bitcoin’s inherent volatility remains a primary risk for ETF investors.
- The increased trading activity spurred by ETFs, including moves by hedge funds and day traders, could also contribute to short-term price fluctuations.
- The introduction of derivatives based on Bitcoin ETFs, such as options, could theoretically lead to increased market liquidity but also potentially heightened volatility through complex mechanisms like “reflexivity squared” and gamma squeezes.
- Significant outflows from Bitcoin ETFs, as seen during periods of market downturn or shifting investor sentiment, can coincide with and potentially worsen price declines.
The Bottom Line:
The general view is that Bitcoin ETF inflows are usually linked to Bitcoin’s price increases and have the potential to contribute to greater price stability in the long run. This is expected to happen by increasing liquidity, broadening investor participation (especially from institutions), and fostering overall market maturity.
However, this relationship is far from simple and can be influenced by many factors, including overall market sentiment, prevailing economic conditions, and breaking regulatory news. While ETFs can absorb some selling pressure, they are not immune to Bitcoin’s typical volatility, and large outflows can occur, potentially amplifying downward price movements.
Therefore, while Bitcoin ETFs represent a major step towards mainstream adoption and may contribute to a more stable market over time, they are unlikely to completely eliminate Bitcoin’s dramatic price swings, especially in the short to medium term. The complex interplay between ETF flows and Bitcoin’s price will continue to be a key dynamic for market observers and participants.
Bitcoin ETFs: Rewriting the Playbook for Traditional Finance
The arrival of Bitcoin Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) has shaken the conservative world of traditional finance, significantly changing how institutional investors view this disruptive digital asset. These regulated investment products have opened new channels for money to flow into the cryptocurrency market, altering investment strategies and reshaping market dynamics in ways once thought unlikely.
Democratizing Access & Deepening Liquidity
Bitcoin ETFs have greatly simplified how both individual and institutional investors can get exposure to Bitcoin. The complexities of direct ownership—managing digital wallets and protecting private keys—are gone. This easier access, through familiar brokerage accounts, has removed previous entry barriers and is widely expected to boost market liquidity. The rush of money from these ETFs could make the market more resistant to the effects of large trades and sudden, sharp price changes. In their first year, new U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs attracted over $36 billion in net inflows, growing to manage around $110 billion in assets. BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) alone impressively drew nearly $1 billion in a single day at one point, with its total cumulative inflows rising past $42 billion.
Reshaping Investment Blueprints
- Wealth Managers on Alert: The very existence of Bitcoin ETFs is forcing wealth managers to seriously consider Bitcoin as a possible part of diversified client portfolios. While some remain hesitant due to volatility concerns, a growing number are exploring strategic allocations, often around 2%, for clients who understand and can handle the risks. Client demand itself is a strong driver, with wealth advisors increasingly asked to explain crypto strategies and their portfolio effects. Some market strategists suggest that even a small allocation to Bitcoin (up to 6%) could improve risk-adjusted returns in a traditionally balanced portfolio.
- Pension Funds Testing the Waters: Pension funds, usually very conservative, are cautiously starting to explore Bitcoin ETFs. In a notable move, the State of Wisconsin Investment Board reportedly invested over $160 million in Bitcoin spot ETFs. Japan’s huge Government Pension Investment Fund is also reportedly looking into Bitcoin and its potential effects on pension portfolios. This tentative adoption by pension funds, which manage trillions of dollars, signals a growing recognition of cryptocurrencies as a legitimate asset class. However, widespread adoption by this cautious group is expected to be slow, likely following a “trickle-down” adoption by brokerages and major investment banks.
- The Broader Institutional Field: Hedge funds, endowments, and family offices are also increasingly using Bitcoin ETFs. These products offer a familiar and regulated way to get exposure to Bitcoin, which many see as a potential hedge against inflation. The entry of these financial heavyweights is predicted to bring in significant capital, potentially leading to increased price stability and market maturity. Reports from the second quarter of 2024 showed a 27% rise in institutional adoption, with hundreds of new firms entering the U.S. spot Bitcoin ETF market. However, it’s also noted that a large part of Bitcoin ETF inflows might be driven by sophisticated arbitrage strategies rather than purely long-term, buy-and-hold belief.
Market Validation & The Price Equation
The regulatory approval and successful launch of Bitcoin ETFs, especially spot versions, by authorities like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), have been widely seen as a strong validation of Bitcoin’s legitimacy as an investable asset. This has undoubtedly boosted investor confidence and is considered a primary reason for the growing demand.
While proving a direct, undeniable causal link is difficult, a broad agreement among analysts suggests that ETF inflows significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. Some research indicates that net flows into Bitcoin ETFs are a strong positive predictor of Bitcoin price levels. The increased demand fueled by ETFs, combined with Bitcoin’s limited supply, can create a powerful mix for price appreciation. For example, after the major approval of Bitcoin ETFs in January 2024, Bitcoin’s price began a significant upward trend.
The Potential for a Calmer Crypto Sea
In the long run, the increasing involvement of institutional investors through ETFs is widely expected to contribute to greater market stability and potentially reduce Bitcoin’s infamous, heart-stopping volatility. Institutional investors often have longer investment timelines and engage in more strategic, long-term asset allocation. Their presence can improve market infrastructure and lessen the kind of extreme price swings that have historically defined the crypto market.
Headwinds and Hurdles Remain
Despite the clear enthusiasm, significant challenges remain. Ongoing concerns about market manipulation, Bitcoin’s inherent volatility, and the liquidity of underlying markets haven’t disappeared. The growing influence of institutional investors could also subtly change Bitcoin’s market dynamics and public perception, potentially causing worries about centralization among some of the cryptocurrency’s original, dedicated supporters. Furthermore, while ETF inflows are undeniably large, a portion may be driven by short-term arbitrage rather than deep, long-term conviction.
An Evolving Financial Frontier
The introduction of Bitcoin ETFs is a major step in bridging the gap between the established world of traditional finance and the dynamic realm of digital assets. It’s creating a more regulated and accessible environment for Bitcoin investing and could very well lead the way for other cryptocurrency-based financial products. As the market matures, ETF issuers may need to innovate beyond just offering the lowest fees to stay competitive, potentially introducing new strategies and options linked to Bitcoin ETFs.
In conclusion, Bitcoin ETF inflows are profoundly reshaping the traditional financial landscape. They are making Bitcoin accessible to more people, fundamentally influencing institutional investment strategies, and contributing significantly to the asset’s legitimization and price dynamics. While the long-term effects are still unfolding, initial trends strongly suggest a significant and potentially transformative role for these pioneering investment vehicles.
Bitcoin ETFs: Charting a Course Towards Mainstream Financial Integration
The arrival of spot Bitcoin Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) in early 2024, especially their high-profile launch in the U.S. market, has been widely seen as a pivotal moment for Bitcoin and the broader cryptocurrency world. These financial products have effectively made access easier, allowing investors to engage with Bitcoin’s price changes through traditional brokerage accounts, thus avoiding the often-complex direct ownership, storage, and security measures. Ongoing inflows into these ETFs are more than just numbers; they represent significant and lasting effects on Bitcoin’s path to mainstream adoption, its changing status as a legitimate asset class, and its growing role in diversified investment portfolios.
Mainstream Adoption: Closing the Chasm
Bitcoin ETFs are serving as a crucial link, connecting the traditional financial world with the rapidly growing crypto market. By offering a regulated and familiar investment product, ETFs are making Bitcoin accessible to a much wider range of investors. This includes individuals and institutions previously put off by security worries or the steep technical learning curve of direct cryptocurrency ownership. This improved accessibility is a powerful force driving wider adoption.
The huge inflows into Bitcoin ETFs since they began, with some estimates exceeding tens of billions of dollars, dramatically show the strong investor interest. This flood of money not only indicates growing confidence in Bitcoin but also contributes to deeper market liquidity and, potentially, greater price stability over time. As more investors participate through these familiar ETF structures, the overall visibility and understanding of Bitcoin are likely to increase, further smoothing the path for widespread mainstream acceptance.
Perception as a Legitimate Asset Class: The Stamp of Approval
The regulatory approval and successful launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs, especially by financial giants like BlackRock and Fidelity, have given Bitcoin a significant measure of legitimacy in the eyes of the traditional financial system. The regulatory oversight that comes with these ETFs provides a level of investor protection and transparency often perceived as lacking in direct crypto investments.
This “market validation” is key in changing Bitcoin’s image from a speculative, niche item into a more credible and recognized part of the global financial landscape. The involvement of established financial players and the strong regulatory framework around ETFs can help address long-standing concerns about market manipulation and the inherent volatility of cryptocurrencies. While volatility remains a characteristic of Bitcoin, the increased institutional participation made possible by ETFs could lead to a more mature and stable market environment over time. Some market analysts see this growing institutional embrace as a clear sign of lasting, long-term demand.
Role in Diversified Investment Portfolios: The New Contender
Bitcoin’s potential as a diversifying agent in investment portfolios is another crucial area greatly affected by the ETF phenomenon. Historically, Bitcoin has often shown a low correlation with traditional assets like stocks and bonds. This quality makes it an attractive option for investors looking to enhance portfolio diversification and potentially hedge against inflation or broader economic uncertainty.
Bitcoin ETFs dramatically simplify including Bitcoin in a diversified portfolio. Investors can now allocate a portion of their assets to Bitcoin through the same brokerage accounts they use for stocks and other ETFs. This streamlined approach makes it much easier to manage and rebalance their holdings effectively.
However, opinions on Bitcoin’s exact role as a long-term investment and a reliable diversifier vary. Some financial advisors urge caution, citing Bitcoin’s inherent volatility and its sometimes-speculative nature. They argue that its value drivers are not as well-understood as those of traditional assets and that it hasn’t consistently performed as a dependable hedge against stock market downturns. Others, however, point to its historical outperformance and its potential as a store of value, particularly in environments with currency devaluation or persistent inflation. Research from institutions like Fidelity suggests that Bitcoin has the potential to boost a portfolio’s returns and may offer tangible diversification benefits, though with the caveat of significant accompanying volatility.
Potential Long-Term Hurdles and Considerations
Despite the clear positive momentum, several challenges and considerations remain:
- The Volatility Beast: Bitcoin’s price remains notoriously volatile, a characteristic that can lead to significant financial losses for investors, even when accessed through an ETF.
- Regulatory Quicksand: The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is still developing globally, and future changes could significantly impact Bitcoin ETFs.
- Manipulation Ghosts: While ETFs operate within a regulated framework, concerns about potential manipulation in the underlying Bitcoin spot market persist.
- Custody Conundrums: While ETFs shield investors from direct custody burdens, the ETFs themselves rely on custodians to safeguard the Bitcoin, introducing its own set of risks.
- The Tracking Gap: An ETF’s performance may not perfectly match Bitcoin’s price due to management fees, trading costs, and other operational factors.
- The Decentralization Dilemma: Some purists argue that the rise of regulated financial products like ETFs could be seen as a subtle move towards centralization, potentially weakening Bitcoin’s original, fiercely decentralized nature.
- Emerging Tech Threats: Financial giants like BlackRock have even highlighted potential long-term risks from advances in quantum computing, which could, theoretically, one day undermine Bitcoin’s cryptographic security.
The Path Forward: A New Chapter for Bitcoin
Sustained inflows into Bitcoin ETFs are very likely to continue reshaping the cryptocurrency market. Market analysts expect further institutional adoption and possibly the development of even more sophisticated crypto-related financial products. The increased liquidity and growing institutional presence could lead to a more stable and mature Bitcoin market, although the asset’s characteristic volatility is unlikely to disappear entirely.
Ultimately, the long-term success and lasting impact of Bitcoin ETFs will depend on a combination of factors. These include continued investor demand, ongoing regulatory developments, the evolution of the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem, and Bitcoin’s inherent ability to navigate potential technological and market challenges. While the initial surge in ETF inflows has undeniably served as a powerful catalyst for Bitcoin’s mainstream journey, the road ahead will require ongoing adaptation, resilience, and maturation.
Bitcoin ETFs: Navigating the Treacherous Waters of Risk
The arrival of Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) has certainly opened new ways for investors to access the growing cryptocurrency market. However, these seemingly convenient investment products also carry a unique set of risks that need careful examination. This closer look uncovers the key dangers associated with Bitcoin ETF inflows, focusing on concentration risk, the potential major impact of large-scale redemptions, and the ever-present counterparty risks linked to custodians.
The Specter of Concentration Risk
One of the biggest worries about Bitcoin ETFs is concentration risk. This danger appears in several important ways:
- Custodian Concentration – Too Few Baskets for Too Many Eggs: A disturbingly large amount of the Bitcoin held by various ETFs is often stored with a very small number of custodians. For instance, reports have shown that Coinbase holds a significant percentage of all Bitcoins owned by Bitcoin ETFs. This heavy reliance on one or just a few custodians becomes a systemic weakness. If a major custodian fails—whether through operational problems, serious security breaches, or even bankruptcy—the effects on the ETFs and their investors could be devastating. This concern is heightened by the fact that many of these custodians are not traditional banks, which usually have deep experience in asset custody.
- Liquidity Provider (LP) Concentration – A Chokehold on Trading?: The crypto ETF space is also marked by a worrying concentration of LPs, with a few firms controlling a dominant share of the market. This dominance can limit healthy competition and potentially lead to price distortions, thereby affecting an ETF’s ability to accurately reflect Bitcoin’s true value. Furthermore, many of these dominant LPs have connections to proprietary trading firms, raising concerns about potential market manipulation or front-running.
- Authorized Participant (AP) Concentration – Another Bottleneck: Similar to the LP situation, a concentration of APs—the specialized firms responsible for creating and redeeming ETF shares—can also introduce significant risks.
The Nightmare Scenario: Large-Scale Redemptions (Outflows)
A sudden, massive wave of redemptions, or outflows, from Bitcoin ETFs can send shockwaves through the market:
- Price Plummets & Volatility Spikes: Sudden and large outflows can force ETFs to quickly sell their Bitcoin holdings. This forced selling can cause a sharp drop in Bitcoin’s price, a particularly alarming situation given the cryptocurrency market’s inherent, often dramatic, volatility.
- Market Disruption & Contagion: Heavy, ETF-driven trading can destabilize futures prices and contribute to increased volatility, potentially leading to widespread investor losses. If an ETF needs to sell its assets quickly due to overwhelming outflows, it could also put undue pressure on bond markets, especially if those ETF assets include cash equivalents like short-term Treasuries.
- Liquidity Shocks – When the Well Runs Dry: Large-scale redemptions, especially when combined with significant moves by major Bitcoin holders (often called “whales”), can trigger severe liquidity shocks, making it hard to trade without causing further price drops.
The Custodian Conundrum: Counterparty Risks Unveiled
Counterparty risk in the Bitcoin ETF ecosystem mainly centers on the custodians—the entities entrusted with the huge responsibility of protecting the underlying Bitcoin.
- Security Breaches & The Hacker Menace: Custodians are prime targets for sophisticated hackers. A successful cyberattack could lead to the permanent loss of Bitcoin held by the ETF, directly affecting the value of investors’ holdings. The infamous Mt. Gox breach, though years ago, serves as a chilling reminder of this constant vulnerability.
- The Insolvency Trap: If a custodian becomes insolvent, a terrifying situation arises: the ETF’s assets could be treated as just general unsecured creditor claims. This could result in devastating losses for investors. This risk is arguably increased by the fact that some custodians may have lower credit ratings than traditional financial giants.
- Operational Failures – The Gremlins in the System: Beyond malicious attacks and financial instability, seemingly ordinary operational failures at a custodian could also severely disrupt an ETF’s ability to manage its Bitcoin holdings effectively.
- The Lack of Traditional Banking Oversight – A Regulatory Grey Zone?: As mentioned before, many Bitcoin ETF custodians are not traditional banks. This often means they may not be subject to the same strict regulatory oversight and large capital requirements as established banking institutions, potentially increasing the risk profile. The SEC’s Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 121 (SAB 121) has been cited as a factor discouraging traditional banks from acting as custodians for Bitcoin ETFs due to its on-balance sheet requirements.
Other Noteworthy Perils Lurking in the Shadows
- Tracking Errors – The Performance Gap: ETFs may not perfectly track Bitcoin’s price. This can be due to various factors, including management fees, bid-ask spreads, and the rebalancing costs in futures-based ETFs.
- Regulatory Quicksand – An Ever-Shifting Landscape: The regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies and crypto ETFs is still developing globally. Unforeseen changes in regulations could dramatically impact the operation, availability, or investor protection mechanisms of these products.
- The Manipulation Maze: The concentration of Bitcoin ownership and the potential for arbitrage between the ETF and the underlying Bitcoin market continue to raise concerns about market manipulation.
- Emerging Technological Threats – The Quantum Menace: Financial giants like BlackRock have even flagged quantum computing as a potential, though perhaps distant, future risk to Bitcoin’s cryptographic security. Theoretical advances in quantum computing could one day break the encryption safeguarding Bitcoin, thereby compromising the entire network.
In Conclusion: While Bitcoin ETFs undeniably offer a more accessible way to invest in Bitcoin, they come with a complex and often unclear set of risks. Prudent investors must be very aware of concentration risks related to custodians and liquidity providers, the potential market-shaking impact of large-scale redemptions, and the significant counterparty risks associated with the entities responsible for protecting the underlying digital assets. A thorough, honest understanding of these many risks is absolutely crucial for making informed investment decisions in this rapidly changing and often unforgiving market.
Bitcoin ETFs vs. Titans: A Fund Flow Showdown with Gold and Tech
The U.S. arrival of spot Bitcoin ETFs in January 2024 wasn’t just a crypto-world event; it was a financial market occurrence that has drawn intense examination and comparison to established ETF giants, particularly those tracking gold and the tech sector. The inflow patterns have been truly dramatic.
Bitcoin ETFs: An Unprecedented Capital Tsunami
- Launch for the History Books: Spot Bitcoin ETFs orchestrated one of the most explosive ETF launches ever. First-day trading volume reached an amazing $4.6 billion. Within a year, these products had absorbed over 1 million BTC (around $40 billion in Assets Under Management – AUM), with net inflows totaling approximately 540,000 BTC even after accounting for significant outflows from Grayscale’s converted Bitcoin Trust (GBTC).
- Asset Accumulation at Ludicrous Speed: BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) has been the clear champion, gathering an incredible $10 billion in AUM in just seven weeks. To compare, the first U.S. gold ETF took over two years to reach that same point. IBIT soared to $50 billion in AUM in only 227 trading days, smashing previous records. By January 2025, spot Bitcoin ETFs had collectively seen net inflows of roughly $36.2 billion. IBIT alone had attracted nearly $38 billion, though this was partly offset by over $21 billion leaving GBTC.
- Dominating the Sector Inflows: In early 2025, U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs were outperforming major traditional ETFs like the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) and Invesco’s QQQ in attracting inflows. They even surpassed the combined inflows of every major sector ETF, including Utilities and Tech ETFs. Year-to-date inflows for Bitcoin ETFs climbed to $3.7 billion, leaving Utilities ETFs ($2.3 billion) and Tech ETFs ($1.0 billion) far behind, while many other sectors saw net outflows.
- Relentless Positive Momentum: Despite some periods of volatility, U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs have shown a consistent and strong positive trend in inflows. For example, in May 2025, they recorded a combined net inflow of $5.89 million, the fourth straight trading day of net positive flows, with BlackRock’s IBIT being a primary driver.
- Institutional Stamp of Approval: The fierce inflows highlight a significant and growing institutional interest in Bitcoin as a legitimate financial asset. Some market forecasters predict that Bitcoin ETFs could attract a staggering 50% more inflows in 2025 compared to 2024, potentially reaching a massive $55 billion.
Gold ETFs: The Steady Tortoise, Safe-Haven Magnet
- A More Measured Start: The first gold ETFs, launched in 2004, gathered $3.45 billion in their first year – a decent sum, but much smaller than Bitcoin ETFs’ $37.5 billion in a similar timeframe. The first U.S. gold ETF, SPDR Gold Shares (GLD), took over two years to pass the $10 billion AUM mark.
- Slow, Sustained Ascent: While Bitcoin ETFs saw a rapid initial surge, gold ETFs followed a path of more gradual but remarkably consistent growth, reaching nearly $20 billion by their ninth year.
- Recent Inflow Dynamics: Global gold ETFs saw outflows of 114 tonnes in Q1 2024. However, Q1 2025 saw a dramatic change, with global physically backed gold ETFs reporting strong inflows of $8.6 billion in March alone, contributing to a large $21 billion in total Q1 flows. North America and Europe were the main sources of these inflows. In India, gold ETFs also registered positive Q1 inflows (+2t) in 2024.
- The “Flight to Safety” Appeal: Gold ETFs often see increased inflows during times of heightened market uncertainty and geopolitical unrest, fulfilling their traditional role as a “safe haven” asset. For instance, record inflows into gold and cash-like ETFs were seen since March 2023, with over $50 billion put into these protective assets. Gold ETF inflows exceeded an impressive $15 billion in Q1 2025 alone.
- Price Impact Post-Launch: The first year after gold ETFs launched saw a relatively small 9% price increase for gold itself.
Tech Sector ETFs: Riding the Performance Wave
- Performance-Tethered Flows: Inflows into tech sector ETFs tend to be closely linked to the performance and prevailing sentiment around the technology sector.
- Recent Trends: In 2023, technology, communication services, and consumer discretionary ETFs successfully attracted money, while sectors like healthcare and energy experienced net outflows. However, by early 2025, year-to-date inflows into Tech ETFs stood at $1.0 billion, significantly behind the Bitcoin ETF powerhouse. In the first half of 2024, technology funds attracted $15 billion, while other sector-equity categories collectively faced outflows.
- Bitcoin ETFs in a League of Their Own (Initially): Bitcoin ETFs have shown a far stronger initial inflow surge compared to their Tech ETF counterparts.
Key Comparative Takeaways:
- Speed of Asset Gathering – No Contest: Bitcoin ETFs, with IBIT leading, have accumulated assets at an absolutely unmatched speed, far exceeding the initial growth of gold ETFs.
- Magnitude of Initial Inflows – A Blowout: The initial rush of money into Bitcoin ETFs dwarfed that seen by gold ETFs in their early days.
- Underlying Market Dynamics: Bitcoin ETF inflows have been fueled by a powerful mix of pent-up demand, growing institutional adoption, and the sheer novelty of a regulated investment product for a new and exciting asset class. Gold ETF flows, on the other hand, are often influenced by broader economic sentiment, inflation worries, and gold’s long-standing role as a store of value. Tech ETF flows are more directly tied to the current performance and future outlook of the technology industry.
- Cannibalization of Older Products: The launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs caused significant outflows from older, often higher-fee products like the Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC), as investors strategically moved to newer, more competitively priced options. This is a common pattern seen with new ETF launches that offer clear advantages over existing investment products.
- Price Impact – A Stark Contrast: Bitcoin prices saw a massive rally (approximately 120%) in the year after the ETF launch, despite an initial “sell the news” dip. Gold, in contrast, saw a more modest 9% increase in its first year post-ETF.
Gazing into the Crystal Ball:
- Market analysts widely expect continued strong inflows into Bitcoin ETFs, with some bold predictions suggesting they could triple the size of gold ETFs within the next three to five years.
- The growth path of Bitcoin ETFs is still in its early stages. Its long-term patterns will be shaped by a complex mix of factors, including regulatory developments, changing market sentiment, and the continued adoption and integration of Bitcoin into the broader financial ecosystem.
In conclusion, Bitcoin ETFs have had a significantly more explosive initial launch and growth phase in terms of inflow patterns when compared to both gold ETFs and tech sector ETFs. While gold ETFs have shown steady, long-term growth and tech ETFs are more directly performance-driven, the sheer speed and amount of money rushing into Bitcoin ETFs highlight a powerful and rapidly developing investor fascination with this groundbreaking digital asset class.
The Global Bitcoin ETF Map: A Dramatic Reshuffling of Inflow Geography
A major shift has occurred in where Bitcoin ETF money is flowing globally, a change largely triggered by the U.S. launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs. The traditional financial centers are now taking the lead in this new asset class, significantly redrawing the world map of crypto investment.
1. Uncle Sam Takes the Crown: U.S. Market Ascendancy
- Overwhelming Market Dominance: The United States now controls an astounding 95.2% of global Bitcoin ETP (Exchange Traded Product) volume. This is a radical change from before 2021 when EMEA (Europe, Middle East, and Africa) was the leader.
- A Tsunami of Inflows: Since January 2024, U.S.-listed Bitcoin ETFs have become a magnet for capital, pulling in nearly $63 billion. In a recent typical week, the U.S. alone accounted for a huge $840 million of the total $882 million that went into global crypto products.
- AUM Skyrockets: The U.S. spot ETF launch supercharged global crypto ETP AUM, causing it to jump by an incredible 178% month-over-month to $42.3 billion by the end of January 2024. By the end of Q1 2024, this figure had soared to an amazing $82.9 billion, a 445% increase from the start of the year.
2. EMEA’s Fading Dominance
- The Former Frontrunner: Before the U.S. introduced its spot ETFs, EMEA was the clear leader, holding a large 70-100% of AUM before COVID and a significant 50-60% between 2021 and 2023.
- A Precipitous Decline: EMEA’s share of global AUM has since dropped to just 12.8%, and its portion of global volume has shrunk to only 4.1%.
3. Snapshots from Other Regions
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) on the Rise: This region had a relatively small share of global AUM before the U.S. spot ETF phenomenon. However, APAC ETF AUM has shown strong growth, increasing by 31% to reach $1.7 trillion in 2024, driven by record net inflows of $149 billion. There’s clear interest in crypto ETF launches across the region, waiting for positive regulatory signals.
- Canada’s Steady Growth: Canada has shown significant growth in its crypto ETF AUM, rising from $3.4 billion in 2023 to $5.6 billion in 2024.
- South America’s Nascent Market: This region also had a minor share of global AUM before the U.S. changed the landscape.
- Country-Specific Flows: Recent data shows Germany attracting over $44 million in inflows and Australia $10 million. In contrast, Sweden experienced outflows of $12 million.
4. The Regulatory Arbiters
- The SEC’s Game-Changing Nod: The approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) was the key event. It legitimized Bitcoin as an asset class for a much broader investor base and effectively opened the floodgates for institutional investment.
- Favorable Climates Attract Capital: Countries with clearer and more supportive crypto regulations are naturally positioned to see more active ETF markets.
- Governmental Tailwinds: Government initiatives are actively boosting ETF growth, particularly in the dynamic Asia-Pacific region.
5. Cultural Currents and Investor Tides
- The ETF Allure: Investor sentiment and the general popularity and preference for the ETF structure play a significant role. The launch of U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs far exceeded initial expectations, powerfully demonstrating this preference.
- Retail vs. Institutional Divide: In the U.S. and Canada, retail investors make up a large majority of the ETF market. Europe, in contrast, sees institutional investors dominating. The Asia-Pacific region shows a more varied and complex split.
- Hunger for Innovation: There’s a consistently strong and clear demand for financial innovation in regions like Asia-Pacific, evident in their keen interest in crypto ETFs.
- The Generational Shift: Younger investors, particularly millennials, are adopting newer ETF categories, including crypto, at much higher rates (69%) compared to baby boomers (46%).
A Note on Tracking: Accurately tracking the exact origin and geographic distribution of all crypto-asset transactions remains a difficult task, given the borderless nature of exchanges and the complexity of trading pairs.
Bitcoin ETFs: A Faustian Bargain for Decentralization and Self-Custody?
The arrival of Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) has undeniably been a major event, pushing cryptocurrency further into the financial mainstream. Yet, this very development has sparked a heated debate among investors, market analysts, and dedicated Bitcoin supporters: are these convenient financial products unintentionally weakening Bitcoin’s core principles—namely decentralization and self-custody—by concentrating large holdings within big institutions?
The Case for Compromised Principles:
- The Specter of Centralized Hoards:
- Concentration Alarms: A primary concern is the worrying concentration of Bitcoin in the hands of a few giant ETF issuers. As of late 2024, spot Bitcoin ETFs collectively held nearly 1 million BTC, about 5% of Bitcoin’s total circulating supply. BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) alone controlled a large part of this, clearly showing how a small number of institutions could potentially have considerable influence over the Bitcoin market.
- Market Sway: This concentration could increase price volatility during times of massive inflows or outflows from these dominant ETFs. Market observers worry that the influence of ETF issuers on market liquidity and price stability will only grow as they continue to gather more Bitcoin.
- Ethos Under Siege: Some vocal critics argue that Bitcoin ETFs, by their very design, directly oppose Bitcoin’s original decentralized nature. They rely on centralized financial systems for trading and storage. The core idea of “not your keys, not your coins,” so central to Bitcoin’s philosophy of financial independence, is arguably weakened when investors entrust their digital assets to ETF custodians.
- The Erosion of Self-Custody:
- Third-Party Dependence: Bitcoin ETFs remove the need for investors to directly own, store, or secure Bitcoin themselves. While this undoubtedly makes it easier for many to invest, it fundamentally means investors do not have direct control over their private keys. This reliance on third-party custodians introduces significant counterparty risk—the constant danger that the custodian could be hacked, face bankruptcy, or be subject to disruptive regulatory action.
- Anonymity & Utility Lost: Investing in a Bitcoin ETF does not offer the same level of anonymity as holding Bitcoin directly, nor does it allow investors to use Bitcoin for peer-to-peer transactions.
- Entangled with Traditional Finance: Prominent critics like Robert Kiyosaki claim that Bitcoin ETFs are just a sanitized version of the traditional financial system, managed by the same Wall Street giants he believes regularly exploit retail investors. Even SEC Commissioner Caroline Crenshaw has voiced concerns, suggesting that linking Bitcoin to traditional finance potentially undermines its original purpose.
The Counterarguments and Nuanced Perspectives:
- Fueling Adoption and Bestowing Legitimacy:
- Mainstream On-Ramp: Bitcoin ETFs provide a regulated and easily accessible way for traditional investors and institutions to get exposure to Bitcoin. This, in turn, can boost liquidity and promote greater market stability. This influx of institutional money has been widely seen as a sign of the crypto market reaching a new level of maturity.
- Market Maturation: Supporters argue that institutional adoption, greatly helped by ETFs, is an unavoidable and mostly positive development. It brings new groups of buyers into the market and improves overall market stability. Some believe this institutional era is a necessary step for Bitcoin to achieve true mainstream integration.
- An Educational Stepping Stone: Certain experts suggest that ETFs could serve as an initial entry point for new investors. These individuals, after becoming familiar, might later explore self-custody.
- Operational Realities and Investor Choice:
- Convenience & Security for Many: For a large number of investors, the complexities of self-custody and the associated security risks are major deterrents. ETFs offer a simpler, and arguably safer, way to invest in Bitcoin, with the fund company expertly handling the details of buying and securing the underlying digital asset.
- Custodians: A Necessary Evil or Essential Service?: Custodians play a undeniably vital role in broader Bitcoin adoption, especially for newcomers who may lack the confidence or technical skills needed for self-custody. ETF issuers typically conduct thorough checks when selecting reputable and secure custodians.
- Bitcoin’s Inherent Resilience: Despite the concentration seen within ETFs, Bitcoin’s underlying decentralized structure makes it extremely unlikely for any single entity to gain complete control over the network.
- The Evolving Crypto-Financial Landscape:
- Coexistence of Models: Some observers believe that Bitcoin can comfortably exist in both institutional and individual hands. Achieving a delicate balance that preserves its core values is seen as essential. Promoting transparency in institutional custody practices and actively educating investors on the principles and practices of self-custody are considered crucial efforts.
- The Rise of Decentralized Alternatives: The emergence of decentralized crypto ETFs, which use blockchain technology and peer-to-peer trading, represents an attempt to preserve the core decentralized nature.
Conclusion: A Precarious Balancing Act
The debate over whether Bitcoin ETFs fundamentally compromise Bitcoin’s core principles is complex and has strong arguments on both sides. While ETFs undeniably introduce some centralization and move away from the self-custody model, they also significantly improve Bitcoin’s accessibility, legitimacy, and mainstream adoption.
Ultimately, the long-term impact of Bitcoin ETFs will be shaped by the continued evolution of the ecosystem. The main challenge is to find a delicate balance that allows for institutional participation while diligently protecting Bitcoin’s foundational principles of decentralization and financial independence. For individual investors, the choice between the streamlined convenience of an ETF and the absolute control offered by self-custody will always depend on their personal priorities, risk tolerance, and understanding of Bitcoin’s core philosophy.
Bitcoin ETF Inflows: Future Forecasts, Catalysts, and Potential Storm Clouds
The U.S. approval and subsequent explosive launch of spot Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) in early 2024 has truly changed the game for the cryptocurrency market. This new financial product has attracted a flood of investor interest and fueled a wave of optimistic predictions for future growth. Reputable financial analysts and institutions are largely positive about continued inflows into Bitcoin ETFs, though they wisely acknowledge potential risks and triggers that could reverse this trend.
Gazing into the Crystal Ball: Future Projections for Bitcoin ETF Inflows
- The Institutional Stampede Continues: A primary driver for projected inflows is the increasing adoption by institutional investors. Asset management giants and sophisticated hedge funds have already invested significantly in Bitcoin ETFs. Market analysts widely expect this trend to grow as more large institutions—including traditionally cautious pension funds, endowments, and even sovereign wealth funds—complete their thorough review processes and begin allocating money to Bitcoin. Indeed, some pioneering state pension funds in the US have already started investing in Bitcoin ETFs.
- Price Targets & AUM Aspirations: Several analysts are boldly predicting that Bitcoin’s price could rise to between $100,000 and $200,000 by 2025, partly driven by the sheer force of strong ETF inflows. Some forecasts even imagine Bitcoin ETFs representing about 7% of Bitcoin’s total circulating supply by 2025 and managing a massive $190 billion in assets. Longer-term projections paint an even more ambitious picture, with some suggesting Bitcoin’s price could hit an incredible $1 million per coin by 2030 or beyond.
- Retail Enthusiasm Endures: While institutional adoption makes headlines, retail investors remain significant contributors to ETF inflows, typically accessing these products through familiar broker platforms. The ease of access and the trusted ETF structure are expected to continue fueling retail demand.
Catalysts Primed to Fuel Further Growth
- Regulatory Clarity & Global Green Lights: Clearer and more favorable regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrencies globally could significantly boost investor confidence and bring in further inflows. The anticipation of regulatory approvals for other crypto-related products, possibly including multi-coin ETFs, could also spark market optimism.
- Macroeconomic Tailwinds:
- The Inflation Hedge Narrative: Bitcoin’s limited supply leads many to see it as a strong hedge against inflation, potentially attracting investors seeking to protect the value of their assets from currency devaluation.
- Monetary Policy Easing: A shift towards easier monetary policy, such as potential interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve, could inject more liquidity into the market and boost demand for risk-on assets like Bitcoin.
- Market Sentiment & Mainstream Embrace: Growing mainstream acceptance of Bitcoin and overwhelmingly positive market sentiment, partly fueled by the success of the ETFs themselves, are crucial drivers.
- Geopolitical Instability as a Demand Driver: In times of heightened geopolitical tension or widespread economic uncertainty, Bitcoin is sometimes seen as a “safe haven” asset, a characteristic that could increase demand.
- Technological Advancements & Ecosystem Expansion: Continued innovation within the cryptocurrency sector, including advances in blockchain technology and the growing popularity of related trends like Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Real-World Asset (RWA) tokenization, can enhance Bitcoin’s utility and overall attractiveness.
- The Bitcoin Halving Effect: The Bitcoin halving, a pre-programmed event that reduces the rate at which new bitcoins are created, inherently limits supply. Historically, this event has been strongly associated with subsequent price increases. Strong ETF inflows coinciding with this programmed supply reduction could be a powerfully bullish catalyst.
Potential Triggers for Significant Outflows: Navigating the Storms
- Market Volatility & Painful Corrections: Bitcoin remains a notoriously volatile asset, and significant price corrections are always possible. Such downturns could trigger a cascade of outflows as investors rush to take profits or reduce risk.
- Negative Regulatory Surprises: Unfavorable regulatory actions or announcements from key regions could severely dampen investor sentiment and lead to substantial outflows.
- Macroeconomic Headwinds Turning Fierce: Contrary to the catalysts, factors such as unexpectedly rising interest rates, persistent inflation fears, or the start of a global recession could lead investors to avoid perceived riskier assets like Bitcoin, thereby triggering ETF outflows. Escalating trade tensions and the threat of new tariffs can also contribute to a broader risk-averse market behavior.
- A Shift in Investor Sentiment: A general decline in investor confidence regarding digital assets, perhaps sparked by major security breaches, high-profile market manipulation scandals, or simply a fundamental shift in risk appetite, could lead to significant withdrawals from Bitcoin ETFs.
- Liquidity Crises: Large, sudden outflows can severely reduce market liquidity, making it increasingly difficult to trade without significantly impacting prices. This can worsen a downward trend, creating a negative cycle.
- The Allure of New Competitors or ETF Structures: While Bitcoin ETFs have been groundbreaking, the emergence of new, perhaps more innovative, investment products or a decisive shift in investor preference towards other digital or even traditional assets could divert capital flows. Some analysts note that while single-token ETFs beyond Bitcoin and Ethereum are unlikely to see massive institutional adoption, retail demand for such products might still exist.
- Unwinding of Specific Trading Strategies: Certain market observers have pointed out that some hedge fund strategies involving Bitcoin ETFs (such as basis trading) could inadvertently lead to selling pressure on the ETFs if Bitcoin’s price were to fall dramatically.
It is important to note that while many analysts remain bullish, some have more conservative or even bearish outlooks. They cite the potential for significant price drops or long periods of stagnation, depending on a complex mix of various market and regulatory conditions. The intricate interplay of these diverse factors will ultimately shape the future path of Bitcoin ETF inflows and outflows.
Bitcoin ETFs: Ripple Effects Across Altcoins and DeFi
The arrival of Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) has undeniably sent tremors throughout the entire cryptocurrency world. The impact isn’t limited to Bitcoin; it’s creating significant waves felt by altcoins and the growing Decentralized Finance (DeFi) ecosystem. This closer look explores the many effects of these transformative financial products.
1. Impact on Bitcoin and Market Legitimacy: The King Gets a Crown
- Institutional On-Ramp Activated: Bitcoin ETFs have served as a crucial, regulated pathway for institutional investors to gain exposure to Bitcoin. This influx of money from financial giants, including BlackRock, has been enormous. In the early months of 2024 alone, Bitcoin ETFs collectively attracted over $41 billion. By May 2024, these inflows had surpassed the $40 billion mark, with BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin ETF (IBIT) leading the way.
- Price Impact & The Supply Squeeze Narrative: The flood of money pouring into Bitcoin ETFs directly influences Bitcoin’s price. As ETF providers must acquire and hold actual Bitcoin, often in deep cold storage, the available circulating supply tightens. This can create a “supply squeeze,” where rising demand meets shrinking available supply, potentially boosting prices significantly.
- Market Maturation & The Quest for Stability: The grand entrance of institutional investors via ETFs is widely seen as a significant sign of the crypto market’s maturity. Supporters argue that this can lead to greater price stability and reduced volatility in the long run, as institutional players often have longer-term investment plans.
- Enhanced Legitimacy & Mainstream Embrace: The regulatory approval and subsequent success of Bitcoin ETFs have significantly boosted Bitcoin’s legitimacy as an investable asset class. This is true in the eyes of institutional and retail investors, and importantly, among regulators. This growing acceptance can pave the way for broader mainstream adoption.
2. Spillover Effects on Altcoins: Riding Bitcoin’s Coattails (Mostly)
- Positive Correlation (The “Rising Tide” Phenomenon): Historically, positive momentum in Bitcoin often translates into gains for the broader altcoin market. The increased liquidity and heightened market activity spurred by Bitcoin ETF inflows can create a “spillover effect,” benefiting altcoins as investor interest and speculative excitement ripple across the entire crypto spectrum. Some prominent altcoins, such as Ethereum and Solana, have indeed seen correlated gains with Bitcoin’s bullish momentum, which many attribute to ETF inflows.
- Shifting Dynamics & The Performance Tug-of-War: While a rising Bitcoin tide can indeed lift many altcoin boats, the relationship isn’t always simple. There can be distinct periods where certain altcoins, particularly Ethereum, show stronger individual performance and attract significant ETF inflows of their own, sometimes even surpassing Bitcoin ETF inflows for specific periods. Conversely, there are times when Bitcoin’s dominance increases, and major altcoins suffer steeper losses than Bitcoin, even amidst generally positive ETF inflows for Bitcoin itself.
- Focus on “Blue-Chip” Altcoins & The ETF Pipeline: The success of Bitcoin ETFs has inevitably led to fervent discussions and keen anticipation for ETFs tracking other major cryptocurrencies, with Ethereum being the next prime candidate. This suggests that institutional interest, once comfortable with Bitcoin, may selectively expand to other established, “blue-chip” altcoins.
- Vulnerability to Broader Market Shocks: Some market analyses suggest that altcoins may be more vulnerable to wider market shocks, such as downturns in the traditional stock market, when compared to the more established Bitcoin.
3. Implications for the DeFi Ecosystem: Indirect Tailwinds and New Frontiers
- Indirect Benefits via Increased Liquidity: The substantial capital inflows into Bitcoin channeled through ETFs can indirectly benefit the vibrant DeFi ecosystem. Increased liquidity in the Bitcoin market can potentially cascade into DeFi platforms and their associated governance tokens.
- Legitimization of the Broader Crypto Economy: The validation of Bitcoin as an institutional-grade asset, largely conferred by the ETF structure, lends a significant degree of credibility to the entire crypto economy, including the innovative DeFi space. This can foster greater mainstream acceptance and attract a wider pool of users and developers to DeFi.
- Potential for DeFi on Bitcoin (BTCFi) to Flourish: Some experts are keenly highlighting the significant growth potential for DeFi solutions built directly on the Bitcoin network itself. Innovations in this growing area, sometimes called “BTCFi,” could unlock entirely new financial tools and attract substantial investment. The total value locked (TVL) in Bitcoin DeFi has already seen substantial growth, partly fueled by infrastructure improvements and the overall positive sentiment wave generated by Bitcoin ETFs.
- Bridging Traditional Finance (TradFi) and DeFi: Bitcoin ETFs can be seen as a crucial stepping stone, helping to bridge the often-separate worlds of traditional finance (TradFi) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi). This convergence could lead to the development of novel hybrid financial instruments that combine elements of both systems.
- Increased Investor Exposure to dApps (via potential ETH ETFs): The potential approval of Ethereum Spot ETFs could further catalyze the DeFi sector. Such a development would implicitly increase investors’ exposure to the vast and rapidly expanding ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps) built on the Ethereum network.
4. Navigating Challenges and Lingering Considerations:
- The Unshakeable Shadow of Market Volatility: Despite the prevailing narrative of market maturation, the crypto market, including assets closely linked to ETFs, remains inherently and often dramatically volatile.
- Concentration of Ownership & The Specter of Market Manipulation: Lingering concerns persist regarding the concentration of Bitcoin ownership and the potential for sophisticated market manipulation, which could also adversely affect ETF markets.
- The Tango with Traditional Markets: Cryptocurrencies, including the leading Bitcoin, can show a discernible correlation with traditional financial markets, particularly with growth-oriented tech stocks. This means that macroeconomic factors and prevailing sentiment in traditional markets can significantly influence crypto prices, regardless of direct ETF inflows.
- ETF Inflows vs. Price: The Occasional Disconnect: There can be peculiar periods where even significant Bitcoin ETF inflows don’t immediately translate into correspondingly large price increases for Bitcoin. Such instances often lead to intense market analysis and debate regarding the complex underlying dynamics at play.
In Conclusion: Bitcoin ETF inflows represent a landmark development, profoundly reshaping the cryptocurrency market. They have significantly enhanced Bitcoin’s accessibility and legitimacy for both institutional and retail investors. This influx of capital is redrawing market dynamics, generally exerting positive price pressure on Bitcoin and constricting its available supply. The effects are rippling outwards, often creating a positive sentiment and attracting capital to the altcoin market, although this relationship can be nuanced, with periods of decoupling or varied performance. The DeFi ecosystem stands to benefit indirectly from the increased liquidity and enhanced legitimacy brought by Bitcoin ETFs, with significant potential for growth in Bitcoin-native DeFi and a broader acceptance of decentralized financial innovations. However, the market remains acutely subject to volatility and external economic influences, underscoring the enduring need for diligent analysis and a comprehensive understanding of these rapidly evolving financial instruments.
The Bitcoin ETF Hype Machine: Media, Influencers, and Narratives Steering the Flow
The rush of investor money into Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) isn’t just about market mechanics; it’s a complex story heavily shaped by the widespread power of media sentiment, the persuasive appeal of influencer marketing, and the strong force of prevailing public narratives. These elements are closely intertwined, together shaping investor perception, fueling demand, and ultimately guiding the inflows and outflows that define these new investment products.
The Unholy Trinity of Influence: Media, Influencers, and Narratives
- Media Sentiment: The Market’s Megaphone: The media’s depiction of Bitcoin acts as a powerful amplifier, significantly affecting investor sentiment. A flood of positive news coverage can ignite speculative excitement, driving up demand and, consequently, prices. Conversely, a wave of negative news can trigger panic selling and send prices down. This cycle of news and investor reaction is a major contributor to Bitcoin’s well-known volatility. Major announcements about regulatory changes, high-profile security breaches, or significant institutional adoption can cause immediate and often dramatic market reactions, directly influencing ETF flows. For instance, positive macroeconomic news can sometimes act as a buffer, lessening the impact of negative investment flows. On the other hand, worrying headlines, such as those about new international tariffs, have been seen contributing to outflows from Bitcoin ETFs.
- Influencer Marketing: The Pied Pipers of Crypto: Crypto influencers, individuals with large online followings and a carefully crafted image of expertise in cryptocurrency, hold considerable sway over their audience’s investment choices. They share information, offer often-simplified market analyses, and make bold predictions that can noticeably move markets. Endorsements from prominent figures can attract huge numbers of investors, leading to sharp, often unsustainable, price changes. New cryptocurrency projects frequently use influencers to create buzz and promote their tokens, though smart investors should stay aware that some of these endorsements may be paid promotions and not entirely unbiased financial advice. The rise of “finfluencers” on popular platforms like YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok is particularly notable. A significant percentage of younger investors now rely heavily on these online personalities for financial guidance, especially concerning volatile crypto assets. Even micro-influencers, with their smaller but fiercely loyal followings, can trigger rapid buying or selling pressure on specific tokens.
- Public Narratives: The Stories We Tell Ourselves About Bitcoin: Dominant narratives around Bitcoin play a crucial role in shaping investor demand and perception.
- “Digital Gold”: The Enduring Tale: This is arguably one of the most widespread and lasting narratives, consistently portraying Bitcoin as a store of value similar to traditional gold, mainly due to its algorithmically limited supply. This narrative strongly appeals to investors seeking a hedge against inflation and geopolitical instability, particularly among younger and more risk-tolerant groups. The launch of Bitcoin ETFs has further strengthened this perception by providing regulated and easily accessible investment channels. However, the “digital gold” narrative is not without its critics, especially when Bitcoin’s price movements correlate more closely with riskier assets like tech stocks rather than acting as a reliable safe haven during broader market downturns. Some critics argue that equating Bitcoin to “digital gold” significantly undervalues its profound technological innovation and its potentially disruptive role in the global financial system.
- “The Inflation Hedge”: A Shield Against Devaluation?: Another powerful narrative positions Bitcoin as a strong defense against the devaluation of fiat currencies. Studies have indeed shown a positive correlation between rising inflation expectations and increased cryptocurrency purchases, suggesting that households see certain cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, as potential inflation hedges. However, the empirical evidence supporting Bitcoin’s effectiveness as an inflation hedge remains mixed and often depends on the context. Some analyses indicate a weak or inconsistent correlation with traditional inflation metrics. Furthermore, Bitcoin’s inherent volatility can make it a decidedly risky hedge for many conservative investors.
- Store of Value/Portfolio Diversifier: Beyond the Hype: Beyond specific crisis-driven narratives, Bitcoin is also increasingly viewed as a legitimate asset class for improving portfolio diversification. The streamlined ease of access provided by ETFs has attracted both retail and institutional investors looking to gain exposure to Bitcoin without the complexities of directly managing the underlying digital asset.
The Direct Impact on Bitcoin ETF Inflows
The complex interplay of these influential factors directly translates into money flowing into and out of Bitcoin ETFs.
- Positive Vibes & Compelling Narratives Fuel Inflows: When media coverage turns bullish, influential figures enthusiastically endorse Bitcoin, and powerful narratives like “digital Gold” or “the inflation hedge” gain widespread acceptance, investor demand for Bitcoin ETFs tends to surge. This was dramatically clear in the record-breaking launch of U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs in early 2024, which quickly gathered over $100 billion in assets under management and attracted significant net inflows. Some market analysts project continued strong inflows, potentially reaching an astounding $55 billion in 2025. The perceived “legitimization” of Bitcoin by major financial institutions offering these ETFs also plays a key role in attracting fresh capital.
- Negative Sentiment & Challenged Narratives Trigger Outflows or Slowdowns: Conversely, a string of negative media reports, persistent regulatory uncertainty, or a significant weakening of dominant narratives (for example, if Bitcoin conspicuously fails to act as a safe haven during a major market crisis) can lead to diminished investor confidence and cause outflows from Bitcoin ETFs. Market corrections, growing disillusionment with the practical uses of crypto beyond speculation, and broader market pullbacks can also contribute to a noticeable slowdown in ETF inflows. Indeed, certain periods have seen significant outflows from Bitcoin ETFs, indicating waning short-term confidence or a strategic rebalancing of portfolios in response to macroeconomic worries.
- The Echo Chamber: The Feedback Loop Effect: There’s also a clear potential for a feedback loop where ETF inflows themselves can influence Bitcoin’s price. This price movement, in turn, can attract more media attention and influencer commentary, further shaping prevailing narratives and subsequent capital flows. Some research suggests a statistically significant, though not always overwhelmingly strong, relationship where positive shocks to ETF flows lead to a persistent positive effect on Bitcoin prices. However, some analysts argue that the dependency might flow in the opposite direction, with soaring Bitcoin prices being the primary magnet attracting retail investors to ETFs.
An Ever-Evolving Landscape of Influence
The launch of Bitcoin ETFs has undeniably marked a significant milestone, making Bitcoin more accessible to a much broader range of investors and further intertwining it with the established mechanisms of traditional financial markets. As the market matures, the influence of media sentiment, influencer marketing, and prevailing public narratives will continue to be critical drivers of investor demand and ETF flows. However, the relative impact of these multifaceted factors may change over time. An increase in financial literacy and broader education about cryptocurrencies could lead to more discerning and less sentiment-driven investment decisions. Regulatory developments will also continue to play a pivotal role in shaping market sentiment and the trajectory of institutional adoption.
In conclusion, a nuanced understanding of the dynamic interplay between media narratives, influencer opinions, and overarching public perceptions like “digital gold” is absolutely essential for comprehending the powerful forces driving investor demand and the consequent inflows and outflows in the burgeoning and often bewildering Bitcoin ETF market.
Beyond Spot: Bitcoin ETF Derivatives and Their Market-Altering Potential
The U.S. regulatory approval for spot Bitcoin ETFs in January 2024 wasn’t just an end; it was the start of a new race: developing sophisticated derivative products based on these pioneering funds. Options, leveraged ETFs, and inverse ETFs are quickly emerging, set to significantly change market dynamics and add new complexities to inflow patterns.
Options on Bitcoin ETFs: Hedging, Speculating, and Deepening the Market
The Rollout:
- Regulatory Hurdle Cleared: The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved options trading on spot Bitcoin ETFs in the fall of 2024. This crucial approval allows investors to trade contracts that give the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell shares of Bitcoin ETFs at a set price (the strike price) before a specific end date.
- Market Debut & Initial Buzz: Options on BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) were among the first available, quickly followed by options on other major Bitcoin ETFs like Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC), Fidelity Wise Origin Bitcoin Fund (FBTC), and ARK 21Shares Bitcoin ETF (ARKB).
- Strong Opening Salvo: The launch of options on IBIT saw impressive trading volume, with a reported $1.9 billion in notional volume on its first day alone. This far surpassed the debut of options on the Bitcoin futures ETF (BITO) back in 2021. A large part of this initial activity was in call options, signaling a generally bullish outlook on Bitcoin’s price.
Potential Market Impact:
- Liquidity Surge & Trading Volume Boom: The availability of options is widely expected to improve market liquidity. It attracts more sophisticated trading strategies, including complex hedging and arbitrage plays, which can lead to a substantial increase in overall trading volume in the broader Bitcoin markets.
- Sharper Price Discovery & Enhanced Efficiency: Options can contribute to more stable prices and more efficient price discovery in the Bitcoin market. By allowing investors to hedge their bets and speculate on price movements, options help create a more balanced ecosystem of “natural buyers and sellers” on both sides of the order book. This, in turn, can potentially reduce excessive volatility.
- Sophisticated Risk Management Tools: Options give investors a versatile set of tools to manage the significant risks associated with Bitcoin’s inherent price volatility. Strategies such as covered calls (selling call options against existing ETF holdings to generate income) and protective puts (buying put options to protect against potential price declines) become readily accessible.
- Greater Institutional Onboarding: The presence of regulated derivative products like options is often a critical requirement for institutional investors. These players rely heavily on such instruments for managing portfolio exposure and implementing complex trading strategies. This could lead to broader and deeper institutional participation in the Bitcoin market.
- Market Maturation & Legitimization: The introduction of options is widely seen as another significant step towards Bitcoin’s maturation as a recognized financial asset, aligning it more closely with traditional assets like gold and stocks. This can boost overall investor confidence and further legitimize Bitcoin within mainstream finance.
Potential Influence on Inflow Patterns:
- Attracting Fresh Capital: Options have the potential to draw new money into the Bitcoin ETF ecosystem. This could come from investors who were previously hesitant due to the lack of sophisticated hedging tools or from those specifically looking to use options-based strategies.
- Paving the Way for Structured Products: A liquid and strong options market can help create innovative structured products linked to Bitcoin ETFs. These could offer customized risk-return profiles, potentially attracting a whole new group of investors.
- Empowering Retail Participation: Options on Bitcoin ETFs make sophisticated trading and hedging strategies more accessible to retail investors, allowing them to manage their crypto exposure through their standard brokerage accounts.
Leveraged and Inverse Bitcoin ETFs: Amplifying Moves, Catering to Traders
The Development Trajectory:
- Early Filings & Anticipation: Even before the landmark approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs, some forward-thinking firms had already applied for leveraged and inverse Bitcoin-linked ETFs. After the spot ETF approval, the development of these leveraged products sped up quickly.
- Notable Launches:
- REX Shares launched the T-REX 2X Long Bitcoin Daily Target ETF (BTCL) and the T-REX 2X Inverse Bitcoin Daily Target ETF (BTCZ) in July 2024. These aim to provide 200% (or -200%) of the daily performance of spot Bitcoin.
- ProShares introduced the UltraBitcoin ETF (BITU) for 2x daily leveraged exposure and the UltraShort Bitcoin ETF (SBIT) for 2x daily inverse exposure to Bitcoin in April 2024.
- Hong Kong saw the launch of Asia’s first inverse Bitcoin futures ETF, the CSOP Bitcoin Future Daily (-1x) Inverse Product, in July 2024.
- The Underlying Mechanics: These specialized ETFs typically use financial derivatives, such as swaps, to achieve their targeted leveraged or inverse exposure. They generally do not hold the underlying asset in the same direct proportion as their stated leverage.
Potential Market Impact:
- Volatility Magnified: Leveraged ETFs, by design, amplify the daily price movements of the underlying asset—in this case, Bitcoin. This can lead to increased short-term volatility in the Bitcoin market, particularly around market close when these ETFs typically rebalance.
- The Peril of “Volatility Drag”: Leveraged ETFs are generally meant for very short-term trading due to the damaging effect of “volatility drag” (also known as compounding decay). Over longer periods, especially in choppy markets, the daily rebalancing can cause the ETF’s performance to differ significantly and often unfavorably from a simple multiple of the underlying asset’s cumulative return.
- Fueling Speculative Trading: Leveraged and inverse ETFs primarily serve active traders and speculators looking to make amplified bets on short-term price movements.
- Market-on-Close (MOC) Impact: The daily rebalancing of leveraged ETFs can significantly impact trading volumes and price movements near market close, potentially worsening price swings during this critical time.
- A New Avenue for Shorting: Inverse ETFs provide a relatively simple way for investors to bet against Bitcoin’s price or to hedge their existing long positions without dealing with the complexities of directly short-selling Bitcoin.
Potential Influence on Inflow Patterns:
- Attracting the Short-Term Trading Crowd: These products are very likely to attract money from traders with a high-risk appetite and a very short-term investment horizon.
- Hedging Demand Surges: Inverse ETFs can see inflows from investors seeking to hedge their existing Bitcoin exposure, particularly when market downturns are expected.
- The Risk of Outflows During Sustained Trends: While leveraged long ETFs might see significant inflows during strong bull markets, long periods of sideways price action or declining prices could lead to substantial outflows. This is due to the negative impact of volatility drag and potential investor disappointment with long-term performance. Conversely, inverse ETFs would likely see outflows in sustained bull markets.
Broader Implications and Lingering Considerations:
- Intensified Regulatory Scrutiny: The development and spread of these more complex derivative products will almost certainly continue under the close watch of regulators, with robust investor protection remaining a top concern.
- The Imperative of Investor Education: The inherent complexity and significant risks of leveraged and inverse ETFs, in particular, require a high degree of investor understanding and financial literacy.
- Robust Market Infrastructure Required: The growth of these sophisticated products will demand strong and resilient market infrastructure, including efficient clearing and settlement processes, to smoothly handle increased trading volumes and complexity.
- Reverberations in the Underlying Spot Market: While Bitcoin ETFs have already shown a clear ability to influence spot Bitcoin prices and trading volumes, the spread of derivatives could further entwine traditional financial markets with the crypto ecosystem. This could potentially lead to new and complex arbitrage opportunities and more intricate price dynamics.
- Competition for Crypto-Native Venues: The increasing availability of regulated, exchange-traded Bitcoin derivatives could intensify competition for crypto-native exchanges that have traditionally dominated this specialized trading space.
In conclusion, the emergence of derivative products based on Bitcoin ETFs represents a natural and perhaps inevitable evolution of this new asset class within the established framework of traditional finance. Options are set to enhance market depth, provide crucial risk management tools, and attract greater institutional participation, potentially leading to more stable and mature market dynamics. Leveraged and inverse ETFs offer specialized tools for sophisticated, short-term traders but also introduce significant risks of amplified volatility and demand a thorough understanding from investors. The overall impact will likely be a surge in trading activity, more diverse and complex inflow patterns, and a further, significant bridging of the gap between the worlds of traditional finance and cryptocurrency markets.
The ETF Engine Room: How Issuers Handle Massive Capital Swings
The surge in popularity of Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), including those venturing into new asset classes like Bitcoin, has highlighted the sophisticated operational systems that allow these investment products to smoothly handle huge inflows and outflows of money. At the heart of this complex process are Authorized Participants (APs), the well-tuned creation/redemption mechanism, and, critically, robust custody solutions—essential for digital assets like Bitcoin.
The Creation/Redemption Mechanism: Fueling ETF Liquidity
An ETF’s remarkable ability to manage large capital movements depends on its unique creation and redemption process. This system is the lifeblood that keeps an ETF’s market price close to its Net Asset Value (NAV), the total value of its underlying assets.
Here’s what typically happens when large inflows (a surge in demand for ETF shares) hit the market:
- Secondary Market Demand Spikes: As many investors rush to buy the ETF, its price on the stock exchange might start to rise above its NAV, creating a noticeable premium.
- APs Enter the Fray: Authorized Participants – usually financial giants like market makers, major investment banks, or large brokerage firms – take action. They are the only entities allowed to create or redeem ETF shares directly with the ETF issuer.
- Assembling the Creation Unit: To meet this growing demand, the AP will carefully acquire the underlying assets that the ETF is designed to track. For a spot Bitcoin ETF, this means buying actual Bitcoin. For an S&P 500 ETF, it involves purchasing shares of all 500 companies in their precise, market-cap-weighted amounts. These assets are then bundled together into a large, standardized block called a “creation unit.” These units are substantial, often consisting of tens of thousands of ETF shares (e.g., 25,000 or 50,000 shares).
- The “In-Kind” Exchange: The AP delivers this “creation basket” of underlying assets directly to the ETF issuer. In return, the ETF issuer gives the AP a corresponding block of newly created ETF shares of equivalent value. This is often an “in-kind” transaction, meaning actual securities (or, in the case of spot Bitcoin ETFs, actual Bitcoin) are exchanged for ETF shares. This method often provides significant tax efficiency. Occasionally, a small cash amount might be included to balance values.
- Shares Hit the Secondary Market: The AP then sells these newly created ETF shares on the open stock market. This action increases the available supply of ETF shares and gently pushes the ETF’s market price back in line with its NAV.
When Capital Flees (Large Outflows): The process simply reverses. APs will buy ETF shares that are trading at a discount to NAV on the secondary market. They then give these shares back to the ETF issuer in designated “redemption units.” In exchange, the AP receives the underlying assets (or cash, depending on the ETF’s structure), which they can then sell. This action reduces the outstanding supply of ETF shares, helping to pull the market price back up towards the NAV.
This continuous, arbitrage-driven process, managed by APs, ensures that ETF prices generally don’t move too far or for too long from the true value of their underlying holdings, even during periods of massive capital inflows or outflows. It also means that the ETF issuer itself is largely protected from the administrative burden of directly handling enormous cash inflows and outflows or being forced into buying or selling underlying assets at bad times, which could disrupt the market.
Managing the Deluge: Operational Nuances of Large Inflows
- Coordination is Key (APs & Market Makers): During times of intense trading volume and surging inflows, ETF managers stay in close and constant communication with APs and market makers. This tight collaboration ensures efficient trade execution without causing significant disruptions in the market price of either the ETF or its underlying assets.
- The Power of Transparency (Portfolio Disclosure): ETF issuers typically disclose their complete holdings daily. This transparency is crucial, as it allows APs to accurately and efficiently assemble the precise creation baskets needed to form new ETF shares.
- Scalability Under Pressure (Operational Infrastructure): ETF issuers and their service providers must have robust and scalable operational infrastructure. This is essential to smoothly handle the increased volume of creation and redemption orders, along with the associated careful record-keeping and strict compliance requirements.
- Ripple Effects on Underlying Assets: Large inflows into an ETF can translate into significant buying pressure on the underlying assets. For highly liquid assets like large-cap stocks, this impact might be absorbed relatively easily. However, for less liquid assets, or in the case of extremely concentrated or niche ETFs, substantial flows can have a more noticeable price impact.
Acquiring Bitcoin for Bitcoin ETFs: A Unique Challenge
For Bitcoin ETFs, the process of acquiring Bitcoin during periods of large inflows presents a unique set of issues:
- Direct Bitcoin Purchases are a Must (for Spot ETFs): When APs create new shares for a spot Bitcoin ETF (one that physically holds Bitcoin), they or the ETF issuer must buy actual Bitcoin in the spot market. This direct, increased demand can noticeably impact Bitcoin’s price, especially if the inflows are large and sustained.
- Sourcing the Bitcoin: APs and issuers need reliable and deep access to Bitcoin liquidity. This is often achieved through established, high-volume cryptocurrency exchanges or via specialized over-the-counter (OTC) desks equipped to handle large block trades without causing excessive market disruption.
- The 24/7 Conundrum (Trading Hours): A key operational difference is that Bitcoin trades around the clock, 24/7, globally. In contrast, ETFs trade only during the set hours of traditional stock exchanges. This mismatch can lead to potential price differences and create challenges in buying Bitcoin at the desired price when APs are assembling creation units for new ETF shares.
Custody Solutions for Bitcoin ETFs: Guarding the Digital Gold
The secure storage of the underlying Bitcoin is absolutely vital for the viability, integrity, and trustworthiness of any Bitcoin ETF.
- Institutional-Grade Guardians (Custodians): Bitcoin ETF issuers always partner with specialized, institutional-grade digital asset custodians. These custodians use a formidable array of advanced security measures to protect the Bitcoin holdings entrusted to them.
- Layers of Security:
- Cold Storage Fortress: A large majority of the Bitcoin is typically held in “cold storage.” This means the private keys controlling the Bitcoin are stored completely offline, protecting them from the constant threat of online hacking attempts.
- Multi-Signature Wallets (Multi-Sig): These sophisticated wallets require multiple distinct private keys to authorize a transaction, adding an important extra layer of security and preventing single points of failure.
- The Insurance Safety Net: Many reputable custodians carry substantial insurance policies designed to cover potential losses from theft or other security breaches. However, the specifics of these policies, including coverage limits and exclusions, can vary significantly.
- Navigating the Regulatory Maze (Compliance): Custodians for Bitcoin ETFs are often subject to strict regulatory oversight, frequently requiring them to be designated as “qualified custodians” under relevant financial regulations. Prominent companies like Coinbase Custody and Fidelity Digital Assets are examples of entities providing these specialized, high-security services.
- Transparency and Audits: Building Trust: Regular, independent audits and transparent, publicly available reporting on Bitcoin holdings are crucial for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring accountability.
- Managing Bitcoin Transfers: Secure & Swift: ETF issuers and their chosen custodians must have robust, proven systems in place to manage the secure and efficient transfer of Bitcoin. This is vital when APs deliver Bitcoin for share creation or when Bitcoin is returned to APs during the redemption process. Nasdaq, for example, has actively worked on proposals to facilitate in-kind creation and redemption for spot Bitcoin ETFs, a process that inherently requires highly secure Bitcoin transfer capabilities.
Navigating the Choppy Waters: Challenges and Considerations
- The Volatility Factor: Bitcoin’s inherent and often dramatic price volatility can pose significant challenges for managing ETF inflows smoothly and for accurately hedging positions.
- The Ever-Evolving Regulatory Landscape: The regulatory environment for crypto-assets, including the growing Bitcoin ETF market, is still developing globally. This can impact operational requirements and influence investor sentiment.
- The Cost of Doing Business (Expense Ratios): The costs associated with secure custody, active trading, and the overall management of a Bitcoin ETF all contribute to its expense ratio. This fee can influence investor returns and is a key point of competition among issuers.
- The Market Impact Equation: While the creation/redemption process is cleverly designed to be efficient, extremely large and rapid inflows into any ETF, including Bitcoin ETFs, can still exert noticeable price pressure on the underlying assets.
In conclusion, the operational backbone enabling ETF issuers to skillfully manage large inflows, particularly for innovative and complex products like Bitcoin ETFs, relies on a sophisticated and well-coordinated interplay between Authorized Participants, the remarkably efficient creation/redemption mechanism, and uncompromisingly secure custody solutions. These critical elements work together to ensure deep liquidity, maintain price stability relative to NAV, and provide investors with regulated, accessible, and increasingly mainstream access to a diverse array of asset classes.
Bitcoin ETFs and the ESG Conundrum: A Thorny Path for Conscious Capital
The rapid rise of Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) has certainly opened new avenues for investors to access the cryptocurrency market. However, this newfound accessibility is deeply shadowed by significant Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) concerns, primarily stemming from the huge energy consumption linked to Bitcoin mining. This single factor heavily influences whether Bitcoin ETFs appeal to the quickly growing group of ESG-conscious investors.
Environmental Alarms: The Insatiable Energy Appetite
The “E” in ESG presents the biggest and most widely discussed obstacle for Bitcoin ETFs. Bitcoin’s “Proof-of-Work” (PoW) consensus mechanism—the complex computational process that secures its network and creates new coins—is notoriously energy-intensive. Immensely powerful computers, often highly specialized hardware known as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), are used to solve complex mathematical problems, consuming vast amounts of electricity.
- Colossal Energy Footprint: Bitcoin mining’s electricity use has drawn alarming comparisons to that of entire countries, such as Sweden or the Netherlands. Some reliable estimates suggest it consumes around 138 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity annually. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) has estimated that cryptocurrency mining operations account for a noticeable 0.6% to 2.3% of total U.S. electricity consumption.
- The Fossil Fuel Dependency: Historically, a large portion of this enormous energy demand has been met by fossil fuels, particularly coal and natural gas. In 2022, an estimated 62% of the electricity powering global Bitcoin mining operations came from these non-renewable sources. This heavy reliance contributes to a significant carbon footprint, with some estimates around 39.8 million metric tons of CO2 per year, though this figure still represents less than 0.1% of total global emissions.
- Tangible Environmental Impact: The energy-hungry nature of Bitcoin mining has reportedly led to the controversial reopening of previously closed coal-fired power plants and other fossil fuel facilities, causing clear environmental and social damage in some areas. A persistent concern is that as Bitcoin’s price rises, its environmental impact correspondingly worsens, as more miners are incentivized to consume even larger amounts of electricity.
The Push for Greener Pixels and ESG-Focused ETFs
Despite these serious concerns, a counter-narrative is emerging, along with real changes in mining practices:
- The Renewable Revolution in Mining: There’s a clear and growing trend towards using more sustainable energy sources in the Bitcoin mining industry. Some reports now indicate that over half (with figures ranging from about 52.4% to 58.9%) of the electricity used by Bitcoin miners comes from sustainable options like hydropower, wind, nuclear, and solar energy. Miners are economically driven to find the cheapest available energy, and renewable energy is becoming increasingly cost-competitive globally.
- Tapping into Wasted Energy: Innovative mining operations are actively exploring ways to use energy that would otherwise be wasted, such as utilizing flared natural gas from oil extraction sites.
- Hardware Efficiency Gains: Continuous advances in mining hardware (ASICs) have led to significant improvements in energy efficiency over the years, although the pace of these technological gains seems to be slowing.
- The Dawn of ESG-Labeled Bitcoin ETFs: Some forward-thinking asset managers are trying to address these ESG concerns directly. For instance, Jacobi Asset Management launched Europe’s first spot Bitcoin ETF with a built-in Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) solution. RECs are market-based instruments representing the generation of one megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity from a verified renewable source. Another notable example is the proposed Nexo 7RCC Spot Bitcoin and Carbon Credit Futures ETF, which plans to mix 80% spot Bitcoin with 20% carbon credit futures, specifically aiming to attract environmentally conscious investors.
- The Carbon Offsetting Gambit: Some Bitcoin ETP (Exchange Traded Product) issuers, such as ETC Group, have announced ambitious plans to achieve carbon neutrality by buying carbon credits to offset the emissions associated with the mining and transaction processes underlying their products.
The “Greenwashing” Skepticism
However, these attempts to give Bitcoin ETFs an ESG-compliant image have been met with considerable skepticism and accusations of “greenwashing.” Critics argue that simply buying RECs does little to meaningfully reduce the direct environmental impact of Bitcoin mining and its substantial, ongoing carbon emissions. The true effectiveness of RECs in genuinely decarbonizing the underlying asset remains a subject of intense and often heated debate.
Beyond Environment: Social and Governance (S&G) Dimensions
While environmental worries dominate the ESG discussion around Bitcoin, the social and governance aspects also need careful consideration:
- Social (S) – A Double-Edged Sword:
- Financial Inclusion Champion?: Supporters passionately argue that Bitcoin can be a powerful tool for promoting financial inclusion. It can provide access to essential financial resources for individuals living in countries with authoritarian regimes or those with severely limited access to traditional banking. Bitcoin facilitates borderless transactions that are inherently resistant to censorship.
- The Shadow of Illicit Activities: Conversely, the pseudo-anonymous nature of Bitcoin has, at times, been linked to illegal activities and money laundering. However, it’s important to note that all Bitcoin transactions are traceable on its public blockchain, and regulatory efforts are increasing globally to combat these harmful uses.
- Governance (G) – Decentralization Meets Regulation:
- The Decentralization Challenge: Bitcoin’s inherently decentralized nature presents unique challenges for traditional regulatory frameworks. However, as the cryptocurrency market matures, regulatory scrutiny is clearly increasing worldwide, which can positively impact governance perceptions. The approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs by influential bodies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) can be seen as a significant step towards greater regulatory acceptance and mainstream integration.
- Transparency Quests: While all transactions are recorded on a public ledger, the governance structures of the Bitcoin network itself and the operational transparency of the entities involved in large-scale mining operations can sometimes lack clarity.
- The Investor Protection Imperative: Regulators globally are increasingly focusing their efforts on strengthening investor protection within the often-volatile crypto markets.
The Appeal (or Lack Thereof) to ESG-Conscious Investors
The significant energy consumption and resulting carbon footprint of traditional Bitcoin mining make standard Bitcoin ETFs a decidedly hard sell for many ESG-conscious investors. For this discerning group, the environmental impact often far outweighs any potential social benefits or perceived governance improvements.
- Investor Reluctance is Real: Many ESG-focused funds and individual investors may consciously choose to avoid Bitcoin ETFs due to their substantial environmental baggage.
- The Demand for Greener Alternatives: The emergence of Bitcoin ETFs that incorporate RECs or carbon credits clearly suggests an attempt by issuers to cater to growing ESG demands. However, the credibility and demonstrable real-world impact of these measures will be absolutely crucial for their acceptance by truly discerning ESG investors.
- A Focus on Broader Blockchain ESG Potential: Some investors might distinguish between Bitcoin specifically and the broader potential of blockchain technology. Blockchain applications focused on improving supply chain transparency, promoting sustainable land management, or other ESG-positive uses might be viewed much more favorably. Ethereum’s successful transition from the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work mechanism to a far more energy-efficient Proof-of-Stake consensus (reducing its energy consumption by an estimated 99%) starkly highlights that not all cryptocurrencies carry the same hefty environmental burden.
Conclusion: A Fork in the ESG Road
Bitcoin ETFs face a huge ESG challenge, primarily driven by the high energy consumption and associated carbon emissions of the Bitcoin mining process. While commendable efforts are underway to increase the use of renewable energy in mining operations and to structure more ESG-friendly Bitcoin ETF products, widespread skepticism around “greenwashing” persists. For Bitcoin ETFs to achieve broad appeal among the rapidly growing ranks of ESG-conscious investors, demonstrable, substantial, and verifiable improvements in the environmental footprint of the underlying asset are absolutely necessary. The social and governance aspects, while also important, are currently overshadowed by these pressing environmental concerns. The continued evolution of regulation and the industry’s unwavering commitment to genuinely sustainable practices will ultimately determine the long-term viability and acceptance of Bitcoin ETFs within a rigorous ESG framework.
Bitcoin ETF Battleground: Fee Wars, Marketing Blitzes, and Market Share Showdowns
The U.S. launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs on January 11, 2024, wasn’t just a regulatory event; it was the start of a fierce competition among financial providers. This new investment product has opened Bitcoin to a much wider audience, including wealthy institutional players, by offering a regulated and familiar structure. The fight for dominance is happening on multiple fronts: fees, marketing, product innovation, and ultimately, market share and inflow distribution.
Fee Wars: The Race to Zero (Almost)
A primary and intense battleground for Bitcoin ETF providers has definitely been fees. In a desperate rush to attract early investors and gain market share, many issuers launched aggressive fee-cutting campaigns, with some even offering temporary zero-fee periods. For instance, BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) strategically began with a reduced fee of 0.12% for the first $5 billion in assets, less than half its initially planned fee. Other players like Franklin Templeton and Bitwise followed, either drastically cutting their rates or introducing attractive introductory fee waivers. VanEck made a particularly bold move, extending its zero-fee offer until January 2026 or until its fund reaches $2.5 billion in assets.
This relentless “fee war” has put intense downward pressure on expense ratios across the entire Bitcoin ETF landscape, a clear win for investors. However, market analysts caution that this fierce competition could lead to a situation where some ETFs never actually become profitable. This could potentially force smaller, less capitalized issuers to close their funds if they fail to attract enough assets under management (AUM). Grayscale’s Bitcoin Trust (GBTC), a giant from the pre-ETF era that converted into an ETF, notably kept a higher fee of 1.5%. Consequently, it saw a significant outflow of funds, although it remains a major player due to its huge pre-existing AUM. Despite these outflows, reports suggest GBTC has remained profitable.
Marketing Blitzes: Building Brands and Cultivating Trust
Sophisticated marketing strategies have also been absolutely crucial in differentiating providers in this crowded field. Established financial giants like BlackRock and Fidelity have skillfully used their globally recognized brand names and extensive existing distribution networks to quickly gain significant traction. Their very entry into the Bitcoin ETF space has been widely seen as a major step in legitimizing Bitcoin as a real asset class.
Marketing efforts have mainly focused on highlighting the unparalleled convenience, deep liquidity, and strict regulatory oversight offered by ETFs. This message particularly appeals to investors who were previously wary of the complexities and perceived risks of directly owning, storing, and securing Bitcoin. Some providers have also cleverly emphasized the potential tax advantages of investing in ETFs compared to navigating the often-unclear waters of direct cryptocurrency holdings.
Product Innovation: Beyond Basic Bitcoin Exposure
While most of the initial spot Bitcoin ETFs offer broadly similar direct exposure to Bitcoin, product innovation is quickly emerging as another critical competitive area. The resounding success of the initial Bitcoin ETFs is widely expected to pave the way for a new generation of more sophisticated crypto-related financial products. These could include leveraged and inverse ETFs, or even ETFs that cover a broader, more diversified range of digital assets.
One early example of such innovation is the Innovator Uncapped Bitcoin 20 Floor ETF (QBF), which launched in February 2025. This product aims to give investors exposure to Bitcoin’s potential upside while also offering a 20% floor against quarterly losses. This type of structured product is designed for investors who are interested in Bitcoin’s explosive growth potential but remain cautious about its inherent, often stomach-churning, volatility. As the market continues to mature, such innovative offerings will likely become increasingly important for attracting specific investor segments and maintaining a competitive edge.
Market Share and Inflow Distribution: The Early Frontrunners Emerge
The intense competitive dynamics have quickly led to a clear concentration of market share among a few dominant players. BlackRock’s IBIT and Fidelity’s FBTC have rapidly established themselves as the undisputed leaders, capturing a large share of inflows and market penetration since their launch. IBIT, in particular, has shown truly remarkable growth, quickly amassing billions in AUM and setting new records as the fastest ETF to reach significant AUM milestones.
Grayscale’s GBTC, despite experiencing substantial outflows mainly due to its higher fee structure and investors strategically taking profits after its conversion, still commands significant AUM. Other providers, such as Bitwise (BITB) and ARK 21Shares (ARKB), have also successfully attracted billions in inflows, although their overall market share remains considerably smaller compared to the leading giants. Conversely, several other ETFs have struggled to gain significant traction, attracting less than $1 billion in inflows within their first year.
The overall success of spot Bitcoin ETFs has been undeniable. These products have collectively attracted tens of billions of dollars in net inflows, cementing their status as the most successful ETF launch in financial history. Daily trading volumes have been consistently substantial, often dramatically outpacing the daily production of new Bitcoins by miners. This huge influx of capital vividly highlights significant and growing investor interest, signaling a clear shift towards larger, more strategic cryptocurrency investments.
Factors Dictating the Flow: Why Capital Chooses Its Home
Several key factors influence how inflows are ultimately distributed among the various Bitcoin ETF providers:
- Expense Ratios – The Bottom Line: Lower fees are a powerful magnet for investors, as they directly impact net returns over the long term.
- Issuer Reputation & Trust – The Familiarity Factor: Investors often prefer well-established financial institutions with a strong, proven track record in successfully managing ETFs.
- Liquidity & Trading Volume – The Ease of Trading: Higher AUM and robust trading volumes generally mean better liquidity and narrower bid-ask spreads, effectively reducing trading costs for investors.
- Marketing Muscle & Accessibility – Getting the Word Out: Effective, widespread marketing campaigns and broad availability on major brokerage platforms play a significant, often underestimated, role.
- Product Structure & Innovation – The X-Factor: While most current ETFs simply track spot Bitcoin, innovative features or unique investment strategies may attract specific investor niches in the future.
- The Regulatory Compass – Navigating Uncertainty: Ongoing regulatory developments and clear, consistent guidance will continue to shape investor confidence and overall market growth.
The Future Battlefield: What Lies Ahead
The competitive landscape for Bitcoin ETF providers is widely expected to remain intensely dynamic. As the market continues to mature, further fee compression is a distinct possibility. The competitive focus may increasingly shift towards sophisticated product innovation, providing value-added services, and skillfully catering to specific, evolving investor needs. The resounding success of Bitcoin ETFs may also serve as a powerful encouragement for developing ETFs tracking other cryptocurrencies, thereby further expanding this growing market. However, Bitcoin’s inherent volatility and the ever-evolving regulatory environment remain key, unavoidable risks for both investors and providers.
The Global Bitcoin ETF Chessboard: Future Regulatory Moves and Inflow Implications
The world of Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) is rapidly and excitingly evolving, with significant potential for future regulatory developments across the globe. These expected changes are set to have a substantial and wide-ranging impact on global inflows into the growing cryptocurrency market, potentially reshaping investment landscapes from Wall Street to Hong Kong.
The Current State of Play: A Watershed Moment Achieved
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission’s (SEC) landmark approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs on January 10, 2024, was truly a pivotal moment. It effectively brought crypto investments into mainstream financial awareness. These innovative ETFs allow investors to get exposure to Bitcoin’s price movements without the complexities of direct purchase and storage, mirroring traditional investment structures and dramatically broadening Bitcoin’s potential investor base. Since their dramatic launch, U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs have seen a flood of inflows, with daily trading volumes surging and the products collectively becoming some of the most popular ETF launches in history. This huge influx of institutional capital signals a significant shift towards larger, more strategic cryptocurrency investments.
Gazing Across Borders: Potential Future Regulatory Developments Globally
- New Jurisdictions Eyeing the Prize:
- Asia’s Awakening: Hong Kong has already made a bold move, launching its first spot Bitcoin and Ether ETFs in April 2024, aggressively positioning itself as a leading crypto hub in the region. This strategic action is widely expected to create a ripple effect, potentially prompting other Asian regions like South Korea and Taiwan to follow. While Singapore currently maintains a more cautious stance on retail access to crypto ETFs, the rapidly changing global landscape could influence future policy decisions. Thailand is also taking a nuanced approach, allowing private funds for U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs for institutional and high-net-worth individuals, though a broader retail offering is not yet on the immediate horizon.
- Australia’s Growing Appetite: Australia has seen growing interest in Bitcoin ETFs, with retail investors leading the initial charge and institutional involvement steadily increasing. The country now has its first spot Bitcoin ETF that directly holds Bitcoin, trading under the ticker IBTC. Market analysts predict that the Australian Bitcoin ETF market could potentially grow to exceed $1 billion within the next one to two years.
- Europe’s Evolving Stance: Europe welcomed its first spot Bitcoin ETF in Amsterdam in August 2023. More recently, the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) has signaled a shift by allowing applications for Bitcoin and Ethereum Exchange Traded Notes (ETNs) to be listed on the prestigious London Stock Exchange, indicating a growing, albeit cautious, acceptance. However, the UK regulator remains hesitant about authorizing Bitcoin ETFs for direct retail investors. Different European nations continue to show varying degrees of regulatory support for crypto ETFs.
- South Africa’s Anticipation: While South Africa has not yet approved spot Bitcoin ETFs, global developments are undeniably increasing pressure on local stock exchanges to consider such approvals, potentially as early as late 2024 or 2025.
- Latin America’s Promise: This region is increasingly seen as an emerging and promising area for cryptocurrency adoption, suggesting fertile ground for potential future ETF approvals.
- Refining Existing Regulations: Fine-Tuning the Frameworks:
- The U.S. Next Steps: Following the initial wave of spot Bitcoin ETF approvals, the SEC may face continued and growing pressure to approve even more sophisticated crypto-related financial products. The initial approval itself was a huge policy shift, coming after numerous rejections and a key court ruling that found the SEC’s reasoning for denying Grayscale’s ETF application to be “arbitrary and capricious.” The SEC Chair has been keen to emphasize that the approval is narrowly specific to Bitcoin as a non-security commodity and does not signal a broader endorsement for other crypto asset securities. Future U.S. regulations could include clearer guidelines for ETF structures, enhanced reporting and compliance rules, and further strengthened consumer protection measures. The approval of options trading on Bitcoin spot ETFs in October 2024 is another significant step in this ongoing evolution.
- The Global Push for Enhanced Investor Protection: Regulators worldwide are expected to sharpen their focus on establishing robust investor protection frameworks. This will likely include requirements for full and fair disclosure, strict rules to prevent fraud and market manipulation, and exacting standards for secure custody solutions.
- The Quest for International Harmony: There is a growing and urgent recognition of the need for greater international coordination of cryptocurrency regulations. Such alignment could significantly ease cross-border ETF offerings and investments, creating a more seamless global market.
The Anticipated Impact on Global Inflows: Unlocking New Capital
- The Institutional Floodgates Open Wider: The increasing availability of regulated Bitcoin ETFs is a powerful catalyst for institutional investors—including hedge funds, asset managers, and family offices—to confidently enter the crypto market. These sophisticated players often prefer the operational simplicity and potentially lower costs of ETFs compared to the complexities of direct cryptocurrency investments. Recent U.S. data vividly shows a significant surge in institutional ownership of Bitcoin ETFs. Some bullish analysts predict that U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs alone could see staggering inflows of up to $220 billion over the next three years.
- Retail Participation Gets a Boost: ETFs make Bitcoin investment far more accessible and less intimidating for retail investors, allowing them to participate through their familiar traditional brokerage accounts, thereby reducing the hurdles of direct purchase and secure storage.
- Deeper Liquidity, Calmer Markets?: Increased inflows into Bitcoin ETFs are widely expected to contribute to greater overall market liquidity and potentially more stable prices, thereby reducing the asset’s infamous volatility in the long run.
- The Price Appreciation Factor: Significant and sustained inflows into Bitcoin ETFs are broadly expected to push Bitcoin’s price upward. Some market analyses even suggest a substantial multiplier effect, where new capital inflows have an amplified impact on Bitcoin’s total market value.
- The Maturation of Crypto as an Asset Class: The growing popularity of Bitcoin ETFs and the associated increase in regulatory oversight are key contributors to the overall maturation and legitimization of the cryptocurrency market as a recognized and increasingly respected asset class.
- Fueling Product Innovation: The resounding success of Bitcoin ETFs could very well pave the way for a new wave of even more innovative crypto-related financial products. This could include ETFs based on other promising cryptocurrencies or those using sophisticated crypto-related investment strategies. For example, the SEC has already approved an ETF that creatively combines Bitcoin with Carbon Credit Futures.
Navigating Potential Headwinds and Lingering Uncertainties
Despite the overwhelmingly positive outlook, several challenges and considerations remain:
- The Regulatory Rollercoaster: The global regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies remains dynamic and often unpredictable, varying significantly across different regions. Potential future policy shifts or unexpected crackdowns could pose significant challenges to the continued growth and operational flexibility of Bitcoin ETFs.
- The Unshakeable Volatility: Cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin leading, are known for their often-dramatic price volatility. This inherent characteristic remains a significant risk for all ETF investors.
- The Custody Conundrum: Ensuring secure and consistently reliable custody solutions for the underlying Bitcoin holdings is absolutely crucial. Any significant security breaches or failures could severely undermine investor confidence and trigger market turmoil.
- The Investor Education Imperative: As a new wave of investors enters the crypto market via the seemingly simple ETF wrapper, ensuring they possess a clear understanding of the unique risks associated with cryptocurrency investments will be of paramount importance.
In conclusion, the global landscape for Bitcoin ETFs is undeniably set for continued expansion and dynamic evolution. As more regions approve these innovative products and existing regulatory frameworks adapt to this new reality, a significant and sustained increase in global inflows, particularly from institutional investors, appears highly probable. This powerful trend is expected to further legitimize Bitcoin as a real asset class and integrate cryptocurrencies more deeply and intricately into the traditional global financial system. However, skillfully navigating the ever-changing regulatory environment and proactively managing the associated risks will be absolutely crucial for ensuring sustained and healthy growth in this exciting new market.
Bitcoin ETFs vs. The Halving: A New Dynamic in Price and Supply
The introduction of Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) has undeniably been a key moment in cryptocurrency’s history. Its influence on how the traditional Bitcoin halving cycle affects price and supply is now a subject of intense research, passionate debate, and considerable market speculation. The old rules might be changing.
The Traditional Halving Cycle: A History of Bullish Catalysts
Historically, Bitcoin halvings, pre-set events occurring roughly every four years, have served as major triggers for significant price increases. The halving process cuts the reward for mining new Bitcoin blocks by 50%. This sharp reduction in the rate of new Bitcoin creation naturally limits supply. Combined with steady or, more often, increasing demand, this “supply shock” has historically sparked bullish market sentiment and led to notable price surges in the months after each halving. For instance, after the 2020 halving, Bitcoin’s price dramatically jumped from around $8,000 to over $69,000 within about a year.
The ETF Effect: Unleashing a New Dimension of Demand
The launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs, particularly their high-profile U.S. debut, has introduced a powerful and entirely new element to Bitcoin’s complex demand dynamics. These ETFs have made Bitcoin accessible to a much broader range of investors. This includes wealthy institutional players who were previously hesitant to invest directly in crypto due to lingering regulatory uncertainties and complex security concerns.
Here’s how ETF inflows are potentially reshaping the halving’s traditional impact:
- Amplified Demand & The “Super Squeeze”: Spot Bitcoin ETFs must hold actual Bitcoin as their underlying asset. As billions of dollars continue to flow into these investment products, ETF issuers are forced to buy large amounts of Bitcoin directly from the market. This constant buying pressure has, at times, resulted in ETF demand greatly outpacing the creation of new Bitcoins by miners. This effect is particularly strong around halving events when the new supply is already being algorithmically reduced. This dual pressure on supply—reduced new issuance from the halving and massively increased buying from ETFs—can create a much more pronounced “supply squeeze” than seen in previous cycles, potentially leading to sharper and more immediate price increases.
- Enhanced Liquidity and the Quest for Market Stability: The large influx of institutional money via ETFs is contributing to increased overall market liquidity and, potentially, greater price stability in the long run. This can make the market more resilient to the impact of large individual trades and sudden, sharp price movements. Some market analysts suggest that institutional involvement, often characterized by longer-term investment strategies, could help reduce the extreme volatility historically associated with halving events.
- Shifting Market Demographics & Investor Behavior: The growing involvement of sophisticated institutional investors through ETFs is tangibly changing the makeup and behavioral patterns of Bitcoin investors. There’s growing evidence of a strengthening trend towards long-term holding, with a significant and increasing portion of Bitcoin’s total supply becoming progressively illiquid as it’s locked away in secure vaults. This “HODLing” behavior, if it continues, further restricts the readily available supply on exchanges, potentially amplifying the market impact of any surges in demand.
- Price Discovery and the “Priced-In” Debate: With the heightened visibility and greatly improved accessibility brought by ETFs, a vigorous debate is underway about whether the halving’s impact is becoming “priced in” by the market much earlier and more efficiently than in previous cycles. Unlike prior cycles, Bitcoin remarkably reached a new all-time high before the most recent halving event—a phenomenon that many market observers attribute directly to the unexpectedly strong and persistent demand generated by the new ETFs.
- The Potential Fading of Cyclicality: Some forward-thinking analysts are now arguing that the traditional four-year Bitcoin cycle, historically heavily influenced by halving events, might be losing some of its predictive power. They suggest that broader market liquidity conditions and overarching macroeconomic factors, now amplified by significant institutional involvement via ETFs, are becoming increasingly influential drivers of Bitcoin’s price.
Current Market Pulse and Expert Commentary:
- Record-Shattering Inflows: U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs have experienced truly explosive growth since their launch in January 2024, quickly amassing significant assets under management and attracting a flood of net inflows. BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) has been a particularly notable leader in this unprecedented capital accumulation.
- Fluctuating Inflow Momentum: While the initial surge in ETF inflows was undeniably substantial, there have been subsequent periods with declining or more volatile inflow patterns. However, recent data from May 2025 has indicated a significant resurgence in positive net inflows for U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs, signaling renewed investor confidence and buying pressure.
- Outperforming Traditional Assets: During certain periods, Bitcoin ETFs have remarkably attracted more inflows than many well-established traditional asset ETFs, signaling a potential paradigm shift in investor appetite and asset allocation strategies.
- The Stark Supply/Demand Imbalance: Market analysts have repeatedly pointed out that ETF buying has, at various times, significantly outpaced the daily production of new Bitcoins by miners. This starkly highlights the immense demand pressure these novel investment vehicles are currently exerting on the available Bitcoin supply.
- A Prevailing Long-Term Bullish Outlook: A strong consensus among many market experts suggests that the powerful combination of continued, robust ETF inflows and the inherent supply-constricting nature of the Bitcoin halving will exert a decidedly bullish impact on Bitcoin’s price over the long term. Some forecasts predict substantial price increases in the coming years, with institutional adoption via ETFs being consistently cited as a key, unassailable driver.
Navigating Potential Risks and Lingering Considerations:
- The Unshakeable Volatility Factor: Despite the theoretical potential for increased stability from institutional involvement, Bitcoin remains an inherently volatile asset. Large, sudden outflows from major ETFs could trigger significant price downturns if issuers are forced to rapidly sell their substantial Bitcoin holdings.
- The Ever-Present Regulatory Shadow: The global regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies and specifically for Bitcoin ETFs continues to evolve. Unforeseen regulatory shifts or announcements could significantly impact investor sentiment and broader market dynamics.
- Concentration Conundrums: While ETFs undeniably broaden access to Bitcoin investment, the increasing concentration of Bitcoin holdings within a relatively small number of large entities (including the ETF issuers themselves) does raise potential, albeit complex, concerns about market manipulation and undue influence.
- The Macroeconomic Overlord: Broader economic conditions, global liquidity dynamics, and significant geopolitical events will undoubtedly continue to influence Bitcoin’s price. These powerful macroeconomic forces could potentially overshadow or intricately interact with the combined effects of the halving and ETF flows.
In Conclusion: The arrival of Bitcoin ETFs represents nothing less than a fundamental and potentially transformative shift in the Bitcoin market structure. While the halving’s core mechanism of systematically reducing new supply remains unchanged, the introduction of ETF inflows is dramatically amplifying the demand side of the delicate supply-demand equation. This new dynamic has the clear potential to alter the traditional price and supply patterns historically associated with Bitcoin’s halving cycles. We may be witnessing a future characterized by more immediate and pronounced price impacts, significantly increased institutional participation, and perhaps, a gradual but undeniable maturation of the entire Bitcoin market. However, the complex interplay of these powerful factors is still unfolding and will continue to be a key area of intense observation, rigorous analysis, and spirited debate for financial journalists, researchers, and market participants alike.
Who’s Buying Bitcoin ETFs? A Look at the Investor Profile
The launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs in early 2024 didn’t just create a new investment product; it significantly changed who invests in cryptocurrency. This new, regulated pathway has attracted a diverse group, from Wall Street giants to everyday retail investors, each with different motivations and risk tolerances. Here’s a closer look at the types of people currently putting money into these groundbreaking funds.
The Demographic Breakdown: A Mix of Old Money and New Blood
- The Institutional Wave: A defining feature of the spot Bitcoin ETF era is the strong influx of institutional investors. This diverse group includes sophisticated hedge funds, large asset managers, registered investment advisors (RIAs), and even some forward-thinking brokerages. By the end of Q4 2024, professional investors (those managing over $100 million in assets) held an astounding $27.4 billion in U.S. Bitcoin ETFs, a remarkable 114% increase from the previous quarter. This institutional group now represents over a quarter of the entire U.S. Bitcoin ETF market.
- Hedge Funds Leading the Charge: Hedge funds have become major players in this new field. Firms like Millennium Management (with a reported $2.6 billion exposure) and Brevan Howard (around $1.4 billion) are among the prominent names making large investments.
- Investment Advisors & Brokerages Joining In: Investment advisors account for a substantial portion of the 13-F holdings (approximately 41%), with over 1,200 different entities participating. Major brokerages such as Jane Street and DRW Securities are also actively involved, mainly providing crucial liquidity and market-making services.
- Retail Investors Still a Dominant Force: While institutional adoption is rapidly growing and making headlines, retail investors continue to be a large and influential part of the Bitcoin ETF market. Some market reports suggest that retail demand still accounts for up to a commanding 80% of the overall market. Spot Bitcoin ETFs have undeniably made it far easier for mainstream individual investors to access Bitcoin through their existing, familiar traditional brokerage accounts.
- Millennials at the Forefront: This demographic shows a strong preference for crypto ETF investments. Over 62% of investors in this growing space belong to the Millennial generation. Younger generations, often called “digital natives,” generally show a greater natural inclination towards Bitcoin adoption and understanding.
- Older Generations (Boomers & Earlier) – A Sleeping Giant?: This demographic, despite collectively holding most of U.S. wealth (an estimated 62%), has historically been slower to adopt cryptocurrencies. However, the familiarity, trusted branding, and perceived regulatory safety of ETFs could potentially attract a larger portion of this wealthier, older, and traditionally more conservative group over time.
- The Gender Imbalance: Historically, cryptocurrency investors have noticeably skewed male. One study focusing on indirect crypto investments (though not specifically ETFs) found that a striking 90% of the crypto investor sample were male. It remains to be seen if the ETF structure will significantly change this long-standing gender gap.
The Psychographic Profile: Motivations and Mindsets
- Risk Tolerance – A Key Differentiator: Bitcoin’s price is notoriously volatile. Investors putting money into Bitcoin ETFs must be prepared for potentially large price swings and the possibility of sharp market downturns. However, some sophisticated investors may see Bitcoin as a strategic tool to introduce managed, asymmetric volatility into an otherwise traditional portfolio.
- The Quest for Diversification: Investors are increasingly looking at Bitcoin as a potential tool for improving portfolio diversification, mainly because its price movements have often historically differed from those of traditional assets like stocks and bonds.
- The Allure of Regulated Exposure: Spot Bitcoin ETFs offer a regulated and familiar investment product. This significantly boosts investor confidence, especially for those who were previously cautious about directly investing in largely unregulated cryptocurrencies. This is a key advantage over previous, often more complex, options like futures-based ETFs or navigating direct crypto exchange trading.
- Convenience and Unparalleled Accessibility: ETFs provide an exceptionally convenient way to get Bitcoin exposure through existing brokerage accounts. This effectively eliminates the often-daunting complexities of managing private keys or navigating the sometimes-confusing interfaces of cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Belief in Bitcoin’s Long-Term Narrative: Many investors are drawn to Bitcoin due to its perceived long-term potential as a resilient store of value or a strong hedge against inflation, often drawing comparisons to traditional gold. Some view it as the “digital gold” of the 21st century.
- Inflationary Fears & Distrust in Traditional Systems: Global macroeconomic trends, such as persistent inflation fears, growing political divisions, and underlying concerns about the stability of traditional banking and fiscal policies, have arguably increased Bitcoin’s appeal as a decentralized, non-sovereign asset.
- Tech-Savviness and Fascination with New Technologies: Younger investors, typically more comfortable and skilled with digital technologies, are often more naturally inclined towards Bitcoin. Some investors are specifically drawn to the revolutionary potential of the underlying blockchain technology.
- The “Fear of Missing Out” (FOMO) Factor: While certainly not a sound investment strategy, the psychological pull of FOMO can play a role for some investors, particularly during periods of rapid, headline-grabbing price appreciation.
- Active Traders vs. Long-Term Buy-and-Hold Investors: The versatile ETF structure caters effectively to both types of investors. Active traders might prioritize high liquidity and tight spreads, while long-term, buy-and-hold investors may place a greater emphasis on minimizing fees.
- Thematic Investing Appeal: Some investors are drawn to Bitcoin as part of a broader thematic interest in disruptive technologies, the future of finance, or the ongoing evolution of digital assets.
Important Caveats and Considerations:
- A Market in Its Infancy: The spot Bitcoin ETF market is still relatively new, and the profiles of its investors may continue to change as the market matures and new products emerge.
- The Power of Low Fees (Fee Sensitivity): Intense competition among ETF issuers has led to relatively low fees, a factor that is highly attractive to cost-conscious investors. Some issuers even implemented temporary fee waivers to capture initial investment flows.
- Indirect Exposure – Not Direct Ownership: It is crucial for investors to understand that investing in a Bitcoin ETF means getting exposure to Bitcoin’s price movements without directly owning the underlying digital asset. This can be a significant advantage for those prioritizing simplicity and security, but a potential drawback for individuals who desire full control over their assets and the ability to trade 24/7.
In conclusion, the investor base for Bitcoin ETFs is remarkably diverse, ranging from large, sophisticated institutions and nimble hedge funds to individual retail investors, with millennials currently leading the way. Key motivations for this interest include the desire for regulated and convenient exposure to Bitcoin, the potential for portfolio diversification, and a fundamental belief in the long-term potential of this groundbreaking asset class. However, the inherent and often dramatic volatility of Bitcoin means these products are generally more suitable for investors who have a higher-than-average tolerance for risk.
Bitcoin ETFs: The Hidden Costs of Tracking Error and Expense Ratios
The growth of Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) has certainly given investors a regulated and much easier way to access the often-volatile cryptocurrency market. However, like all complex investment products, Bitcoin ETFs come with their own important considerations, mainly the issues of tracking error and expense ratios. These seemingly small factors can significantly affect an investor’s net returns and play a key role in product selection, thereby directly impacting fund inflows and the competitive landscape.
Decoding the Jargon: Tracking Error and Expense Ratios Explained
Tracking Error: The Performance Gap This important metric measures the difference between the ETF’s performance and Bitcoin’s actual, real-time price. Several complex factors contribute to tracking error in Bitcoin ETFs:
- Management Fees and Inescapable Operational Costs: These are unavoidable costs related to the day-to-day running of an ETF. They directly contribute to any difference from the underlying asset’s raw performance.
- Rebalancing Acts and Transactional Friction: For Bitcoin futures ETFs, the recurring cost of “rolling over” futures contracts (selling expiring contracts and buying new, longer-dated ones) can lead to significant tracking errors. This issue is especially noticeable if new contracts are consistently more expensive than the expiring ones, a market condition known as “contango.” Spot Bitcoin ETFs, which physically hold actual Bitcoin, generally have lower tracking errors compared to their futures-based counterparts.
- The Perils of Pricing Discrepancies: Spot Bitcoin ETFs often track a specific reference rate that is typically calculated only once per day. This can lead to noticeable, though usually temporary, differences between the ETF’s traded share price and Bitcoin’s continuously changing real-time market value.
- The Liquidity Factor of Underlying Assets: If an ETF invests in less liquid Bitcoin-related assets (though less common for pure Bitcoin ETFs), it can result in frustrating differences between the ETF’s market price and Bitcoin’s true underlying value.
- The Volatility Amplifier: Bitcoin’s inherent and often dramatic price volatility can also worsen tracking errors, making precise tracking more difficult.
Expense Ratios: The Annual Toll This represents an annual fee charged by the ETF provider to cover the fund’s operational and management costs. It’s always expressed as a percentage of the fund’s total assets. Expense ratios directly reduce an investor’s potential returns; even seemingly tiny differences in these fees can compound over time to significantly impact long-term profitability. Bitcoin ETFs, particularly the more complex futures-based types, can sometimes have higher expense ratios than traditional equity ETFs. This is due to the additional costs of managing cryptocurrency assets, including specialized custody arrangements and increased security measures.
The Bottom Line: Impact on Net Investor Returns
Both tracking error and expense ratios directly reduce potential investor returns.
- Expense Ratios – The Certain Cost: These are a direct, unavoidable, and ongoing cost of investing in the ETF. A higher expense ratio means a larger portion of potential returns is consumed by fees each year. Over a long investment period, these costs compound, potentially leading to a substantial difference in the final investment value compared to a similar fund with a lower expense ratio.
- Tracking Error – The Uncertainty Factor: A significant tracking error fundamentally means the ETF is not accurately reflecting Bitcoin’s true performance. If the ETF consistently underperforms Bitcoin due to persistent tracking error, investors are effectively missing out on potential gains they might have otherwise achieved.
The Investor Calculus: Influence on Product Selection and Capital Flows
Modern investors are increasingly savvy and very aware of the profound impact that fees and performance metrics have on their overall investment outcomes.
- Lower Fees: The Siren Song for Assets: Generally, ETFs with lower expense ratios are inherently more attractive to investors, especially when comparing funds that supposedly track the exact same underlying asset, such as Bitcoin. This undeniable investor preference has sparked intense competition among Bitcoin ETF providers, leading some to offer exceptionally low fees, or even temporary fee waivers, to attract substantial initial inflows.
- Tracking Accuracy: Beyond Just Low Fees: While low fees are undoubtedly desirable, they do not, by themselves, guarantee superior returns if the ETF suffers from a high and persistent tracking error. Investors, therefore, also carefully consider how closely an ETF manages to track Bitcoin’s actual price movements. Spot Bitcoin ETFs are often preferred over their futures-based counterparts precisely for their potential to track Bitcoin’s spot price more accurately and with less friction.
- The Gravitational Pull of Fund Size and Liquidity: Larger ETFs with substantial assets under management (AUM) often signal greater investor confidence and can lead to better market liquidity (the ease with which shares can be bought and sold without significantly impacting the price). Higher liquidity typically means narrower bid-ask spreads, which directly reduces trading costs for investors.
- The Trust Factor: Issuer Reputation: The reputation, experience, and track record of the ETF issuer, particularly in managing crypto-related or commodity ETFs, can also significantly influence investor choice and confidence.
The landmark launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs in the U.S. in early 2024 triggered a massive wave of inflows, vividly indicating strong investor demand for regulated, accessible Bitcoin investment products. Market data clearly shows a discernible trend of investors favoring Bitcoin ETFs that offer lower fees and more efficient underlying structures. This is evidenced by the substantial inflows into products like BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) and the corresponding outflows from older, higher-fee products. This dynamic strongly highlights that while the initial novelty and unprecedented accessibility of Bitcoin ETFs undoubtedly drove the first wave of inflows, ongoing product selection and sustained capital allocation will likely be heavily influenced by demonstrable cost-effectiveness and consistent performance accuracy.
In Conclusion: Tracking error and expense ratios are absolutely critical factors for any individual or institution considering an investment in Bitcoin ETFs. They directly and materially impact net returns, and investors are increasingly using these metrics to meticulously compare competing products. As the Bitcoin ETF market continues to mature and evolve, fierce competition on fees and a demonstrable, unwavering ability to accurately track Bitcoin’s price will likely be the key determinants of which funds ultimately attract the most significant and sustained inflows in this exciting and rapidly expanding new frontier of finance.