Ethereum gas fees tank to 5-year lows: What’s behind the drop?

- Ethereum mainnet gas fees drop amid low network demand.
- We assess the role of Ethereum layer 2s in the declining gas fees and decongesting the mainnet.
Ethereum [ETH] has had quite the reputation over the years for having expensive transaction fees, a situation that has driven many users to layer 2 networks.
But, recent findings reveal that Ethereum gas fees have been declining.
High gas fees on the Ethereum network have been a limiting factor, discouraging many from participating in DeFi within the mainnet.
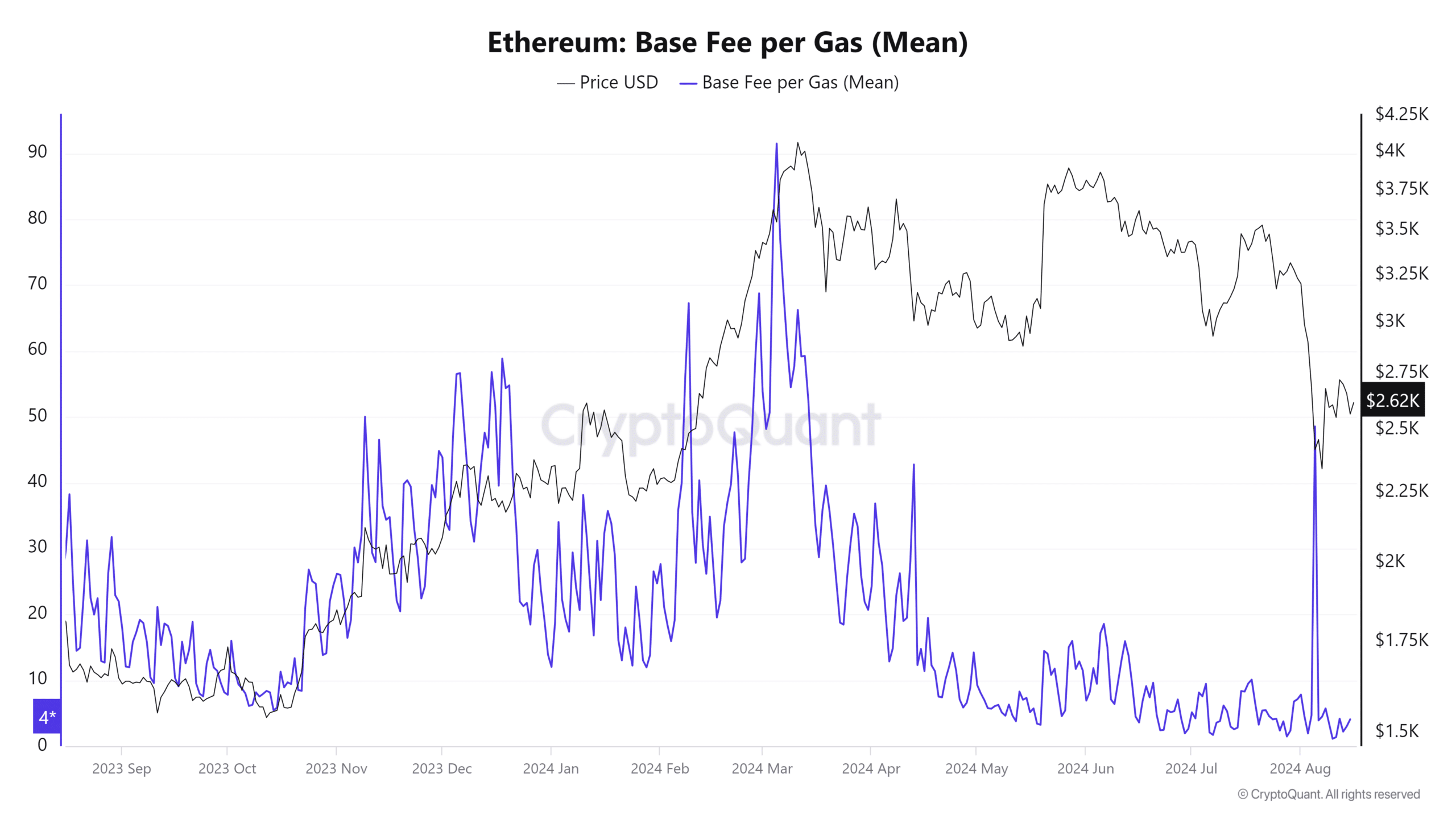
However, recent findings revealed that gas fees recently dropped to their lowest levels in the last five years.
AMBCrypto found that gas fee dropped to as low as 1.38 Gwei on the 11th of August. For context, the mean base gas fee on the network went as high as 91.51 Gwei on the 5th of March.
This was just before prices peaked in March, followed by a strong pullback.
Why are Ethereum gas fees declining?
One of the most plausible explanations for this outcome is the decline in network activity. Ethereum gas fees are heavily influenced by supply and demand, and this is often evident during high network activity.
Gas fees have historically rallied when demand or transactions go up, and the opposite is also true. This was evident during the latest market crash when a spike in transactions selling ETH was observed.
This resulted in a gas fee surge.
Ethereum gas fees hitting a new low may have also been influenced by Layer 2 activity.
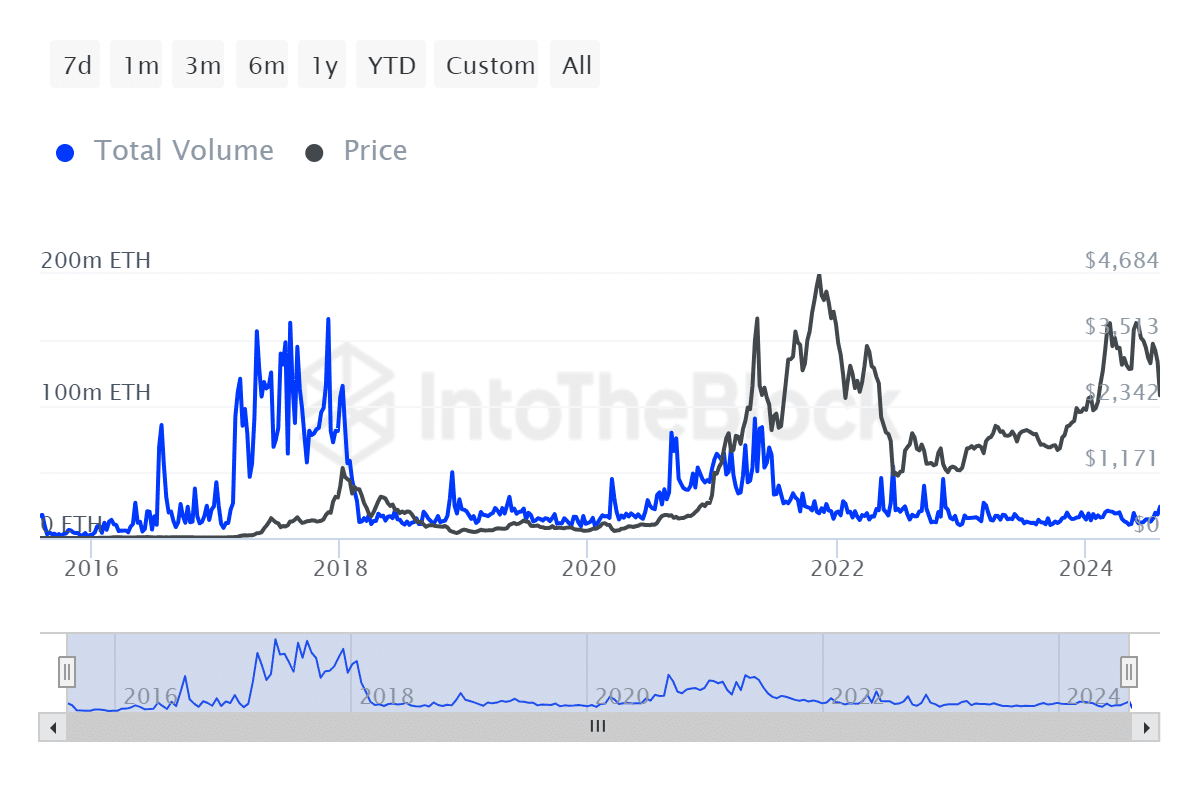
The Ethereum Layer 2 environment is now more developed than it was in 2018, thus offsetting the mainnet congestion that drove up prices. This is evident in the Ethereum network transaction volume.
Ethereum transaction volume at the height of the 2017 bull run peaked at 165.97 million ETH. The figure was considerably moderate during the 2021 bull run, with volume peaking at 90.44 million ETH.
The highest transaction volume recorded so far in 2024 was 20.19 million ETH, just before the altcoin reached an YTD high.
Based on the transaction volumes, it is clear that the rapidly growing Ethereum layer 2 environment has a significant impact on the Ethereum mainnet.
Read Ethereum’s [ETH] Price Prediction 2024-25
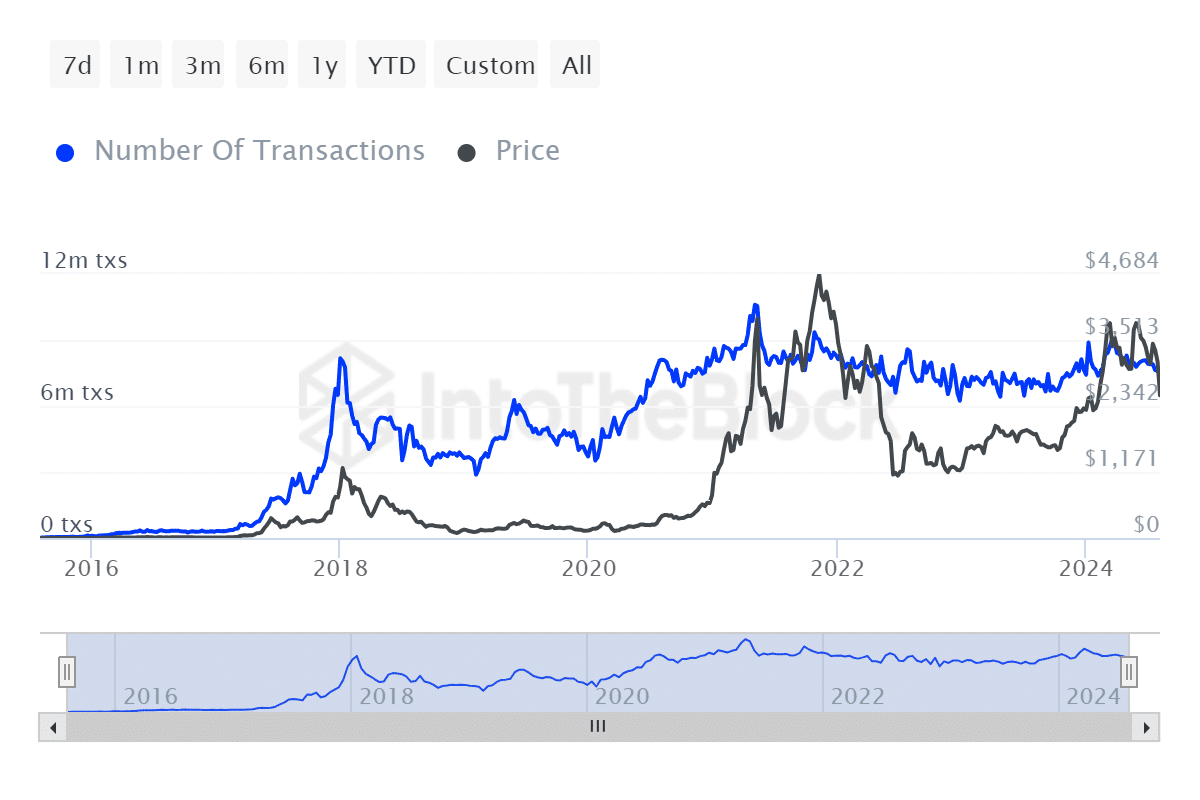
Congestion was down considerably in the last few years, hence the declining gas fees. This was further supported by positive transaction growth over the years, courtesy of positive user growth.
Ethereum transactions maintained an overall positive trajectory over the years. An inverse correlation compared to gas fees, highlighting the impact of layer 2 networks.